Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Distance Protection?
A distance protection element measures the quotient impedance (V/I), considering the phase angle between the voltage V and the current I.
Line distance relays constantly measure the line voltage and current, constantly performing Ohm’s Law calculations to measure the load impedance flowing through the relay at any moment in time.
If the measured impedance is less than the line impedance, there must be a fault on the line and the relay should trip with no intentional time delay.
In the event of a fault, sudden changes occur in measured voltage and current, causing a variation in the measured impedance.
The measured impedance is then compared against the set value. Distance element will trip the relay (a trip command will be issued to the CB associated with the relay) if the measured value of the impedance is less then the value set.
Distance protection is used to protect transmission lines . It is a non unit protection.
Why Distance Protection ? Why not Overcurrent relay?
The reach of over current relay is function of Source Impedance which varies considerably, making it difficult to get fast and Selective tripping. So , distance protection is used as a primary protection.
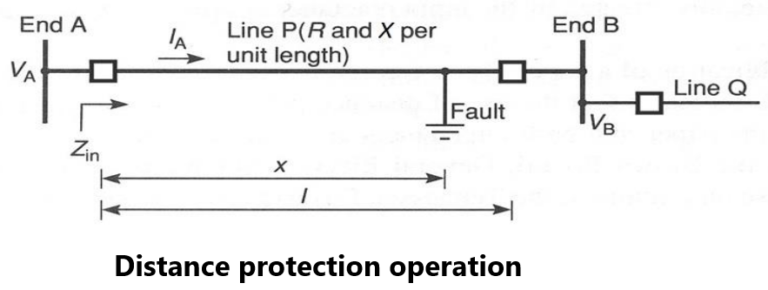
In Fig. the impedance measured at the relay point A is Zin , where x is the distance to the fault (short circuit), and R and X are transmission line parameters in per unit length. The line length is l in the fig.
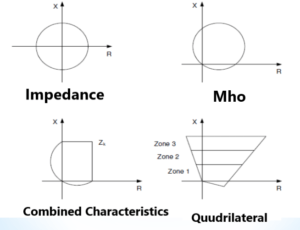
Operating characteristics of distance protection elements are usually represented using R-X diagrams.
Various operating Characteristics
Protective relays respond and operate according to defined operating characteristic and applied settings.
Each type of protective relay has distinctive operating characteristic to achieve implementation objective: sensitivity, selectivity, reliability and adequate speed of operation.
Required information for Protective Setting
Line Parameters
Line length, voltage level, conductor size and conductor type used for local as well as remote substations.
This information is used to calculate the parameters (positive and zero sequence resistance, reactance) for each section.
Maximum load current or apparent power (MVA) corresponding to the emergency line which can be obtained from the table of standard conductor rating (available in each utility).
The number of conductors in a bundle has to be taken into consideration.
Conductor Specifications if not available, refer to CEA manual ‘Annexure-V, Table 1(a), Line parameters’.
Transformer Parameters
The manufacturer’s positive and zero sequence impedance test values have to be obtained.
The transformer nameplate normally provides the manufacturer’s positive sequence impedance values.
Voltage ratio, MVA rating, %Impedance value
CT & PT Ratios
Obtain the CT & PT ratios as indicated on the protection diagrams.
For existing circuits, it is possible to verify the ratios indicated on the diagrams by measuring the load currents on site and comparing with a known ratio.
Arc & Tower footing resistance
Used in resistive reach calculation.
Advantages of Distance Protection
Speed and Reliability: Distance protection is fast because it provides a direct measurement of fault location and does not require the relay to rely on time-delay mechanisms or communications with other relays, which can be affected by line conditions or other factors.
Selective Fault Isolation: It allows for selective fault isolation by only disconnecting the faulty section of the line, leaving the healthy portions of the transmission system operational. This enhances system reliability and minimizes disruptions.
No Need for Voltage Reference from the Fault Side: Unlike overcurrent protection, distance protection does not require voltage reference from the faulted side of the line. This makes it particularly useful for protecting long and complex EHV transmission lines.
Coordination with Other Protection Relays: Distance protection can be coordinated with other protection schemes, such as overcurrent, differential, and directional protection, to provide comprehensive protection for the entire transmission network.
Works in Different Fault Conditions: Distance protection is effective for both symmetrical and asymmetrical faults (e.g., line-to-line, line-to-ground faults) and can be configured to provide different fault type settings.


Pingback: What is Power Swing. Their effect on distance relay and detection method
I haven¦t checked in here for some time because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I will add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Perfectly pent articles, Really enjoyed reading.
Thanks a Lot!
keep learning
What i don’t realize is actually how you’re not actually a lot more neatly-preferred than you may be right now. You are very intelligent. You already know thus significantly when it comes to this matter, produced me personally consider it from so many various angles. Its like women and men are not fascinated except it’s one thing to accomplish with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. Always deal with it up!
It¦s actually a nice and helpful piece of information. I¦m happy that you shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I really like your writing style, good information, appreciate it for putting up :D. “Nothing sets a person so much out of the devil’s reach as humility.” by Johathan Edwards.
Hey very nice website!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also…I am happy to find a lot of useful information here in the post, we need work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Unquestionably consider that that you stated. Your favourite reason appeared to be at the net the simplest factor to keep in mind of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while other people think about worries that they just don’t recognize about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing with no need side effect , other people can take a signal. Will probably be again to get more. Thanks
Perfect piece of work you have done, this internet site is really cool with good info .
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive learn something like this before. So good to find someone with some unique ideas on this subject. realy thanks for starting this up. this website is one thing that’s needed on the net, somebody with just a little originality. useful job for bringing something new to the internet!
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is simply great and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the rewarding work.
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what website owners wrote but this site is very user pleasant! .
With havin so much content do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or copyright infringement? My website has a lot of completely unique content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it looks like a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my authorization. Do you know any methods to help reduce content from being stolen? I’d definitely appreciate it.
A lot of of whatever you mention is astonishingly accurate and it makes me ponder the reason why I hadn’t looked at this with this light before. This piece truly did switch the light on for me personally as far as this specific subject matter goes. However at this time there is 1 issue I am not too cozy with so while I try to reconcile that with the actual central idea of your position, allow me see exactly what the rest of the subscribers have to say.Well done.
Thanks for another informative blog. Where else could I get that kind of information written in such an ideal way? I have a project that I am just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such information.
What’s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & aid different customers like its aided me. Great job.
What i do not realize is in truth how you are not really a lot more well-appreciated than you might be now. You’re so intelligent. You realize thus considerably in terms of this topic, made me in my view consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be fascinated unless it is something to do with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs nice. All the time handle it up!
An impressive share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a little analysis on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I found it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I feel strongly about it and love reading more on this topic. If possible, as you become expertise, would you mind updating your blog with more details? It is highly helpful for me. Big thumb up for this blog post!
I have been checking out some of your posts and i can claim clever stuff. I will make sure to bookmark your website.
I like this site so much, saved to favorites. “American soldiers must be turned into lambs and eating them is tolerated.” by Muammar Qaddafi.
It¦s actually a great and helpful piece of info. I¦m satisfied that you just shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
You are my breathing in, I possess few web logs and often run out from to brand : (.
whoah this blog is magnificent i love reading your articles. Keep up the great work! You know, a lot of people are searching around for this info, you can help them greatly.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Wonderful work! That is the type of information that are supposed to be shared around the internet. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this submit higher! Come on over and discuss with my site . Thank you =)
Excellent beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your website, how can i subscribe for a blog web site? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
I really enjoy reading on this website , it contains fantastic blog posts.
I keep listening to the news talk about receiving boundless online grant applications so I have been looking around for the best site to get one. Could you tell me please, where could i acquire some?
Somebody essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the very first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I amazed with the research you made to create this particular publish amazing. Great job!
Thanks for every other wonderful article. The place else could anybody get that kind of information in such a perfect means of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I am on the search for such information.
I love the efforts you have put in this, thankyou for all the great content.
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
Utterly pent articles, appreciate it for entropy. “Life is God’s novel. Let him write it.” by Isaac Bashevis Singer.
Right now it looks like Movable Type is the preferred blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
It’s exhausting to seek out knowledgeable folks on this matter, however you sound like you understand what you’re talking about! Thanks
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thank you, I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your web site?
It?¦s really a cool and helpful piece of info. I am glad that you shared this useful info with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Simply desire to say your article is as surprising. The clarity on your publish is simply excellent and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep up to date with imminent post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
We absolutely love your blog and find many of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind creating a post or elaborating on some of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome blog!
Hmm it appears like your website ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any recommendations for rookie blog writers? I’d genuinely appreciate it.
As I website possessor I think the written content here is really wonderful, thankyou for your efforts.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I’m very glad to see such fantastic information being shared freely out there.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. It extremely helps make reading your blog significantly easier.
Very efficiently written post. It will be useful to anyone who usess it, including me. Keep up the good work – looking forward to more posts.
Pingback: Safety Requirements for EHV Transmission Line Construction
F*ckin’ remarkable things here. I’m very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
Pingback: Distance relay Zone of Protection - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Phase Overcurrent setting of Transmission line
Pingback: Distance Relay Coordination with case study
Simply wanna tell that this is handy, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
It’s onerous to find knowledgeable individuals on this subject, however you sound like you recognize what you’re speaking about! Thanks
It is actually a nice and helpful piece of info. I am satisfied that you shared this useful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I have been surfing on-line greater than three hours these days, but I never discovered any interesting article like yours. It is beautiful value sufficient for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content material as you did, the net will probably be much more helpful than ever before.
Great contribution
Loved this piece
As soon as I observed this website I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
A large percentage of of what you claim happens to be supprisingly appropriate and that makes me wonder why I had not looked at this with this light previously. This particular piece truly did turn the light on for me as far as this particular issue goes. Nevertheless at this time there is actually just one factor I am not necessarily too cozy with and whilst I attempt to reconcile that with the actual central idea of the position, permit me observe what the rest of your subscribers have to point out.Well done.
Glad to be one of the visitors on this awing site : D.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Nice blog right here! Also your site rather a lot up fast! What web host are you the use of? Can I get your associate hyperlink to your host? I wish my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
It’s onerous to find knowledgeable folks on this matter, but you sound like you realize what you’re talking about! Thanks