Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Electric Drive
An electric drive is defined as a form of machine equipment designed to convert electric energy into mechanical energy and provide electrical control of this process.
Nowadays, in electric power stations generating large amounts of electric energy for agriculture, industry, domestic needs, and electrified traction facilities and in driving all kinds of working machines, electric motor is essential, which is the predominant type of drive so the term electric drive being applied to it.
Electric drive becomes m ore popular because of its simplicity, reliability, cleanliness, easiness, and smooth control. Both AC and DC motors are used as electric drives; however, the AC system is preferred because:
I t is cheaper.
I t can be easily transmitted with low-line losses.
I t can be easy to maintain the voltage at consumer premises within prescribed lim its.
It is possible to increase or decrease the voltage without appreciable loss of power.
In spite of the advantages of AC motor, sometim es DC motor is used because:
In some processes, such as electrochemical and battery charging, DC is the only type of power that is suitable.
The speed control of DC motors is easy rather than AC; thus, for variable speed applications such as lift and Ward Leonard system , the DC motors are preferred.
DC series motor is suited for traction work because of high starting torque.
Block Diagram of Electric Drive
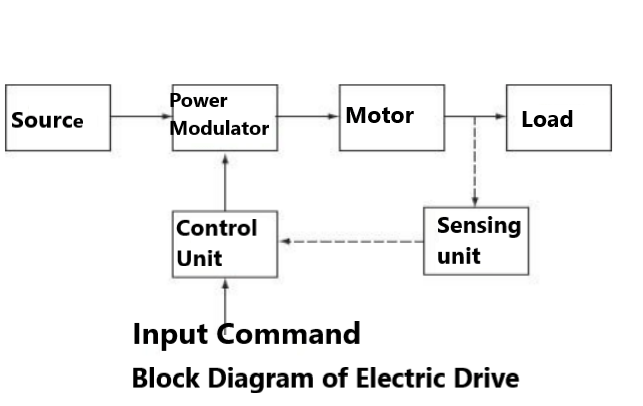
Source
1-Ø and 3- Ø, 50-Hz AC supplies are readily available in most locations. Very low power drives are generally fed from 1 Ø source; however, the high power drives are powered from 3- 3 source; some of the drives are powered from a battery.
Power modulator
Power modulator perform s the following functions:
It modulates flow of power from the source to the motor is impart speed torque characteristics required by the load.
It regulates source and motor currents within permissible values, such as starting, braking, and speed reversal conditions.
Selects the mode of operation of motor, i.e., motoring or braking. o Converts source energy in the form suitable to the motor.
Electrical motors
Motors commonly used in electric drives are DC motors, induction motors, synchronous motors, blushless DC motors, stepper motors, and switched reluctance motors, etc. In olden days, induction and synchronous motors were employed mainly for constant speed drives but not for variable speed drives, because of poor efficiency and are too expensive. But in nowadays, AC motors employed in variable speed drives due to the development of semiconductors employing SCRs, power transistors, IGBTs, and GTOs.
Load
It is usually a machinery, such as fans, pumps, robots, and washing machines, designed to perform a given task, usually load requirements, can be specified in term s of speed and torque demands.
Control unit
Control unit controls the function of power modulator. The nature of control unit for a particular drive depends on the type of power modulator used. When semiconductor converters are used, the control unit will consists of firing circuits. Microprocessors also used when sophisticated control is required.
Sensing unit
Sensing unit consists of speed sensor or current sensor. The sensing of speed is required for the implementation of closed loop speed control schemes. Speed is usually sensed using tachometers coupled to the motor shaft. Current sensing is required for the implementation of current limit control.
Advantages of electric drives
- They have comparatively long life than the mechanical drive.
- It is cleaner, as there are no flue gases, etc.
- It is more economical.
- They have flexible control characteristics.
- There is no need to store fuel or transportation.
- It requires less maintenance.
- Do not pollute environment.
- It is the reliable source of drive.
- The electrical energy can be easily transmitted by using transmission lines over long distances.
- Available in wide range of torque, speed, and power.
- High efficiency.
- Electric braking system is much superior and economical.
- Smooth speed control is easy.
- They can be started instantly and can immediately be fully loaded.
- They can operate in all the quadrants of speed torque plane.
- Being compactness, they require less space.
- They can be controlled remotely.
Disadvantages of electric drive
- The non-availability of drive on the failure of electrical power supply.
- It cannot be employed in distant places where electric power supply is not available.
Recent trend in Electric Drive
Automation and Robotics: In industrial automation, electric drives are being used to power robotic arms, conveyors, and other machinery. These drives are highly flexible and can be precisely controlled, contributing to increased production speeds and precision.
Smart Grid Integration: Electric drives are becoming key components in smart grid systems, enabling better load management and integration with decentralized energy sources.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN): The use of wide-bandgap semiconductor materials like SiC and GaN in power electronics is increasing. These materials allow for higher switching frequencies, reduced losses, and better thermal performance in electric drives, especially in high-performance applications like electric vehicles and industrial systems.
Advanced Inverters: Inverters, which convert DC power from batteries into AC power for motors, are becoming more advanced, featuring higher efficiencies and better control algorithms, enabling smoother and more reliable motor performance.
Solid-State Relays and Drives: There’s a trend toward the development and adoption of solid-state drives in high-performance applications. These drives are more durable, have faster switching times, and require less maintenance than traditional mechanical drives.
Battery and Energy Storage Integration: As battery technology improves (with higher energy densities, quicker charging times, and longer lifespans), electric drives are increasingly being integrated with energy storage systems to create more autonomous and efficient systems.
Internet of Things (IoT): Electric drives are being integrated with IoT technologies to enable real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. This helps improve reliability, reduce downtime, and lower maintenance costs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI algorithms are being used to optimize motor control, predict faults, and adjust performance in real-time, ensuring that electric drives are operating at their peak efficiency.
Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (EVs): Electric drives are increasingly being used in the automotive sector, particularly in hybrid and fully electric vehicles. Advances in electric motors, battery technology, and drive control systems are making EVs more efficient and affordable.
Wind and Solar Power: Electric drives are also integral to the operation of renewable energy systems. They are used in wind turbines and solar power generation systems, improving efficiency in power conversion and energy storage.


I do not even understand how I finished up right here, however I thought this put up used to be great. I do not recognise who you are but certainly you are going to a well-known blogger when you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
wonderful points altogether, you simply gained a brand new reader. What would you recommend about your post that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
Thanks a Lot!
share my post to your friends to appreciate my work.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Dead indited subject material, regards for entropy. “He who establishes his argument by noise and command shows that his reason is weak.” by Michel de Montaigne.
Great tremendous issues here. I am very happy to look your article. Thank you so much and i am having a look forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
hi,
thanks for appreciation. Now, my focus on spread my website content to more readers.
To boost my moral, Please share my website to your friends and subscribe my Insta/Telegram/Whatsapp group.
Great contribution
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.