Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of renewable energy, the quest for efficient and sustainable power generation methods has led to the development of hybrid solar systems. These systems ingeniously combine solar energy with other renewable sources, not only enhancing the reliability of power supply but also contributing significantly to the global transition towards clean energy. This chapter delves into the fascinating realm of hybrid solar systems, exploring their various facets and the benefits they offer in the pursuit of a greener future.
Integrating Wind Power with Solar for Increased Reliability
As the sun bathes the Earth in its abundant energy, and the wind sweeps across landscapes with its kinetic force, combining these two formidable sources of power seems only logical. Hybrid solar wind systems are designed to harness the complementary nature of solar and wind energy.
While solar panels thrive under clear skies, wind turbines tend to perform better during cloudy periods or at night when solar output is reduced. By merging these two sources, the system’s power generation becomes more consistent and reliable.
Integrating solar and wind components within a single system requires careful consideration of technical challenges. One such challenge is the fluctuating nature of both solar irradiance and wind speed. Engineers and researchers have tackled this issue by implementing advanced control systems that manage the distribution of power based on real-time conditions.
Additionally, hybrid systems often employ energy storage solutions, such as batteries, to store excess energy generated during optimal conditions for use during periods of lower energy generation.
The advantages of integrating solar and wind power are manifold. Firstly, this hybrid approach increases the overall capacity factor of the system, leading to a more consistent and stable power supply.
Secondly, it allows for better utilization of resources, as the system can generate power from both sources simultaneously or individually, depending on the prevailing weather conditions. Finally, hybrid systems demonstrate an increased potential to deliver power when it’s needed the most, which is a critical factor in ensuring a reliable energy supply.
Hybrid Solar Generators: Biomass and Micro Hydro
Biomass energy, derived from organic materials, has long been a reliable source of power in various forms. When combined with solar energy, the result is a potent hybrid system that offers benefits beyond what each source can provide individually. Biomass can be burned to generate heat, which in turn can be converted into electricity. By coupling this process with solar power, the overall efficiency of the system increases significantly.
Micro-hydroelectric systems, which harness the energy from flowing water, have proven to be an effective means of generating electricity, especially in areas with access to streams or rivers. When integrated into hybrid solar setups, micro-hydro systems can function as a supplementary power source during times when solar energy generation might be limited. This combination ensures a more continuous energy supply, reducing dependency on a single source.
While the hybridization of solar energy with biomass and micro-hydro systems offers promising advantages, it’s crucial to address potential environmental and resource-related concerns. The sustainability of biomass sources, for instance, requires diligent management to prevent deforestation or depletion of natural resources. Similarly, the ecological impact of micro hydro installations on aquatic ecosystems necessitates careful planning and adherence to environmental regulations.
Grid-Interactive Systems and Net Metering
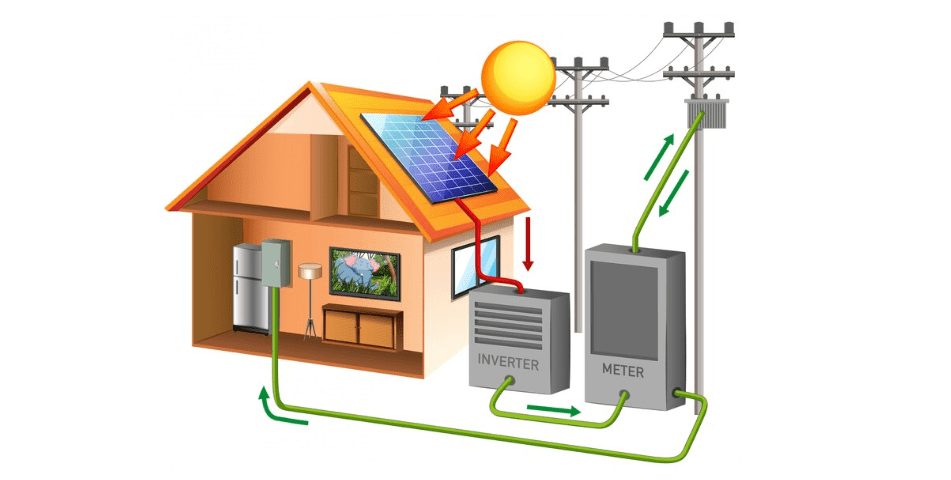
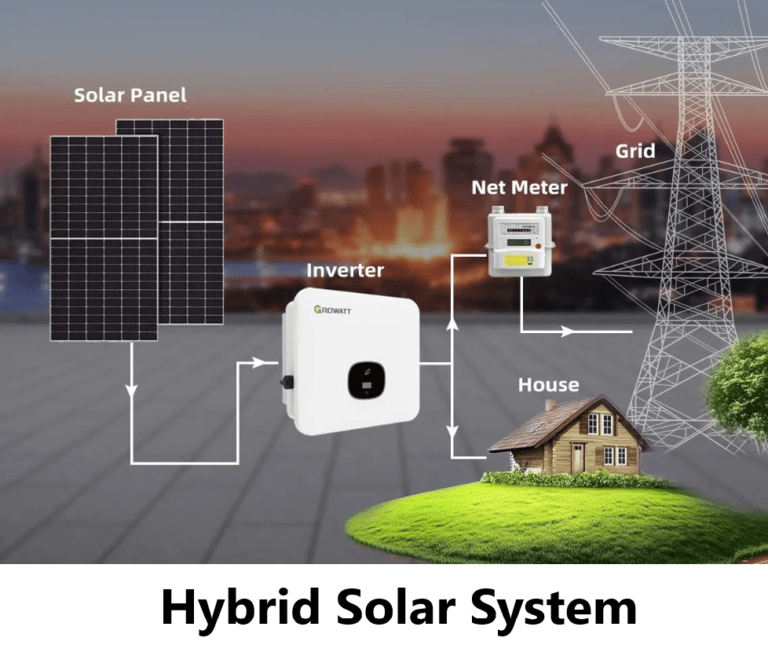
In an era where consumers are becoming increasingly conscious of their energy consumption patterns, grid-interactive hybrid solar systems have emerged as a means of active participation. These systems enable users to not only generate their own power but also interact with the grid. Excess energy generated by the system can be fed back into the grid, earning consumers credits or payments, depending on the net metering policies in place.
Net metering, a cornerstone of grid-interactive systems, allows consumers to strike a balance between their energy generation and consumption. When the hybrid solar system generates surplus energy, it is fed into the grid, effectively “spinning the meter” backward. During periods when the system’s energy generation is insufficient, such as at night, consumers draw energy from the grid. The net energy consumed or generated determines the final billing or credit received.
While the concept of net metering holds significant promise, its implementation faces certain challenges. Regulatory frameworks and policies vary from region to region, impacting the feasibility and benefits of net metering. Moreover, technical aspects such as metering accuracy and grid compatibility need to be meticulously addressed to ensure smooth integration and fair compensation.
Hybrid solar systems that incorporate other energy sources represent a remarkable stride in the pursuit of a sustainable energy future. By synergizing the strengths of solar power with wind, biomass, and micro hydro systems, these hybrid configurations offer enhanced reliability, stability, and environmental benefits.
The integration of grid-interactive systems and net metering further empowers consumers to actively engage in the energy ecosystem while contributing to the reduction of carbon footprints on a global scale. As technology continues to advance and renewable energy solutions evolve, hybrid solar systems stand as a testament to human ingenuity and our commitment to forging a cleaner and greener world.