Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Battery?
Battery Is a device that stores or releases electrical charges by chemical reaction (chemical to electrical and vice versa).
The charges (current) that gets stored or released depends on the battery chemistry, physical design and environmental conditions.
Batteries are generally referred as Electro-Chemical Energy Storage Devices and its storage capacity is expressed in Ah
Unlike in a generator where electricity is due to the flow of electrons, in a battery the flow is due to both electrons (in the external circuit) and ions (inside the battery)
Battery are also called an energy conversion device
Batteries of varying capacities are used depending on the applications:
Off-grid applications
Grid-tied Home Systems and
Batteries in Off-Grid Residential PV Systems

Batteries an integral part of off-grid system serving the following purposes:
To store excess energy generated during the day for use in the night or during low sunshine/ cloudy days
Provide stable power to loads
Supplement energy during cloudy days.
Supply high surge currents to loads
To utilize solar as a backup to grid power
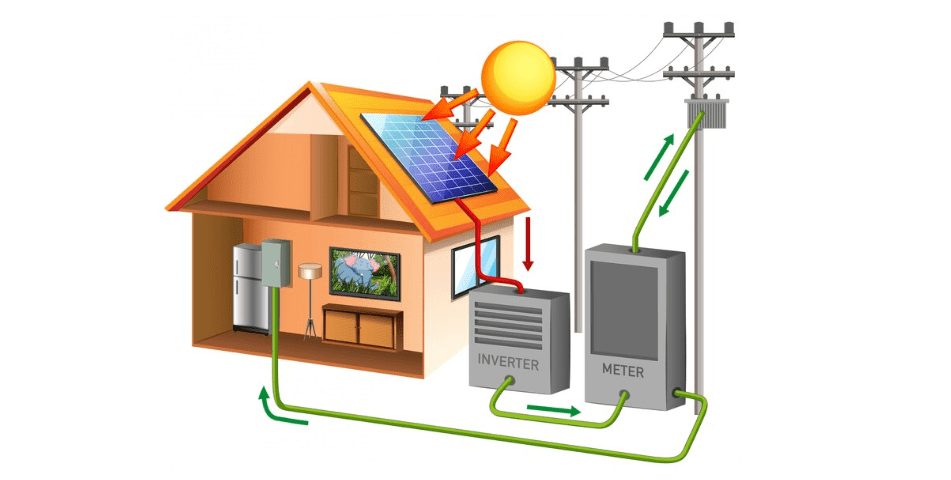
Batteries in Grid Tied Home PV System
Grid Tied Home PV systems
Generate power to feed home loads and any excess is exported to the grid
When home load demand is more than generation, grid power is imported to make up for the deficit; and also in the night when solar energy is not available.
The system does not have battery storage.
The inverter in the system that converts Solar DC Power to AC requires the presence of grid to which it synchronizes its output voltage and frequency.
The Islanding protection in the inverter, a very important safety feature, requires that the inverter disconnect itself when the grid fails.
Whenever the inverter gets disconnected the generated solar power gets unutilized.
A Hybrid inverter that features the islanding safety and also has a DC –DC converter requires a battery to ensure that the generated solar power is not lost during grid failure.
Battery Installation in Residential System
Ensure that the area around the battery is clean and no combustible material is stored around.
Install battery rack / cabinet and place batteries securely on them as per manufacturer’s instruction.
If the battery is kept inside metal rack earth the enclosure properly.
Ensure that the racks are protected against corrosion from acid spill.
Provide adequate clearance: Leave room for free flow of air, maintenance, and fire safety (follow IS standards).
Anchor for earthquake/impact: In seismic areas, use additional restraints.
Use properly sized, fused, and color-coded cables (ensure polarity is correct).
Interconnect batteries as per design.
Install disconnect switches and breakers: On both DC and AC sides for safety andmaintenance Install charge controller as per manufacturer instructions.
Test the Charge controller for its function.
Commission the batteries safely as per the manufacturer instructions batteries.
Batteries in PV Power Plants
With the growing RE integration to the grid, Batteries and other Energy Storage systems have become important.
To overcome the intermittent nature of solar radiation that renders solar power infirm and makes the grid balancing even more complicated.
It enables peak shaving and load shifting in the grid and helps stabilize the grid with large RE Integration.
Ensure reliability of the grid.
Provide power instantaneously, from standby to full power in less than a second, unlike other spinning reserves.
Enhance the efficiency of the overall grid.
Batteries are the most preferred energy storage system as it offers many advantages.
Batteries for Power Plants are large in size and for safe and reliable operation have far more control and safety systems and is called Battery Energy Storage System (BESS).
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
Components of a BESS

Enclosures
Are protective housings designed to safely store and manage batteries
Are designed to be compact, modular, and scalable, often incorporating features like thermal management, fire safety systems, and robust construction for different environments.
Are available in standard sizes/ Custom made sizes
Commonly 3 types of Enclosures available
Indoor BESS, Outdoor cabinet BESS, Outdoor Container BESS
Energy Storage Device
The battery is the energy storage device that is charged by RE resources and/or the grid and is a core component of the BESS System.
Among various batteries, the most widely used is the Lithium-Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries for its superior safety, longer lifespan and better performance in high-temperature environments.
Monitors & Control
Battery Management System (BMS)
Monitors in Real-time battery status and ensures battery safety, reliability, and stability of operation
Provides real-time information/alerts to users on operating status, operating parameters & anomalies.
It is also enables operating costs and revenue analysis of the energy storage system
Environmental Monitoring and Control
Detects abnormal surrounding conditions using temperature sensors, door sensors, flooding sensors, smoke sensors etc. and sends signals to the Environmental Control Module
Environment Control module controls the operation of precision air conditioner, air cooling duct and automatic control system providing an ideal temperature and humidity environment for batteries during charging and discharging.
Fire Suppression System
Since fire is a major hazard, a reliable fire suppression system ensures the safety of the energy storage system designed to prevent electrical fires.
Power Conversion System (PCS)
The PCS is a inverter used is a bi-directional inverter/charger converting Solar DC to AC to feed to the grid and Grid AC to DC to charge the battery
Breaker, Switch & Transformer
The BESS contains a DC breakers on the DC side of the system and AC Breakers on the AC side of the system (AC and DC breakers should not be interchangeably used for safety reasons)
Transformer ensures the output of the BESS fits the client’s requirements on AC voltage.
Benefits of BESS
Generation Capacity is capacity to consistently meet electricity demand, ensuring a reliable supply of power at all times (during peak demand & disruptions included).
Flexible Capacity is the ability of a power system to adjust its electricity generation and/or consumption patterns in response to changing demands or grid conditions.
Virtual transmission / distribution capacity is the ability to increase power flow on an existing transmission line without physically upgrading it by using energy storage to shift power flow timing.
Ancillary services include frequency regulation, voltage control, peak shaving, operating reserves, congestion relief, and power smoothing.
Black start is the process of restoring power to an electric grid after a complete or partial shutdown without relying on the external power transmission network.
How Battery maintenance carried in Solar Plant?
Battery System Maintenance
State of Health SoH Monitoring: Regularly check capacity fade, internal resistance, and performance against manufacturer benchmarks
Cell Balancing Inspection: Ensure the BMS is balancing cells correctly inspect for cells welling, corrosion, or discoloration
Thermal Monitoring: Verify uniform temperature distribution Overheating or hotspots indicate cooling failure or cell degradation
Connection Tightness: Check electrical terminals for loosening, oxidation, or corrosion
Power Conversion System (PCS)
Inverter/Converter: Health Checks Inspect filters, cooling fans, capacitors & insulation. Confirm DC/AC conversion efficiency
Firmware Updates: Keep control and communication firmware up to date for performance and cybersecurity
Harmonics and Grid Compliance: Ensure harmonic distortion is within limits and that system responses meet grid codes
Thermal Management System
Coolant or HVAC Checks: For liquid cooled systems, check coolant levels, flow rate, and leaks For air cooled systems, clean or replace filters and ensure fan function
Thermal Insulation: Inspect enclosures for weather damage or insulation degradation, especially in harsh climates
Fire Detection Suppression
System Test: Functionally test smoke, gas, and thermal detectors
Suppression Agents Check: check agent levels and valve integrity inspect piping for leaks
Emergency Protocols: Ensure manual release stations and alarms work and staff are trained on protocols
Battery Management System (BMS)
Data Review: Regularly analyze logs for fault events, temperature anomalies, or unexpected
Behavior
Communication Integrity: Check fiber ethernet wiring, communication protocols (Modbus, CAN, etc.), and redundancy.
Calibration: Periodically calibrate voltage &temperature sensors.
Structural Environmental Maintenance
Container/Enclosure Integrity: Inspect for water ingress, corrosion, or rodent intrusion
Grounding Lightning Protection: Ensure all protective systems are intact and test for continuity
Cable Trays and Conduits: Look for wear, sagging, or UV damage in exposed areas
SCADA and Remote Monitoring
Data Sync: Ensure real time monitoring and alerting is functional
Cybersecurity: Patchvulner abilities rotate passwords and review access logs
Reporting: Generate and review periodic performance reports and alarms.
Routine Testing & Audits
Thermal Imaging: Use to detect abnormal heat patterns in batteries, cables, or PCS
Insulation Resistance Testing: Especially after heavy rain or storms
Factory Field Service Recommendations: Follow OEM guidelines for testing intervals and component replacement
Safety Drills and Training
Staff Training: Routine training for O&M staff in emergency scenarios, system operation, and fire safety.
Mock Drills: Practice response to thermal runaway, blackout, or PCS fault


I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again
Thanks for Appreciation, Please share my website to your social group
You made some good points there. I did a search on the subject and found most guys will consent with your website.
Pingback: Fault Finding in Electronic Circuit board
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thx again!
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble. You are wonderful! Thanks!
Very informative and fantastic complex body part of written content, now that’s user pleasant (:.
I will immediately snatch your rss as I can not find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly permit me recognise so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Smooth and clear
Hello.This post was really fascinating, especially because I was investigating for thoughts on this topic last couple of days.
oficjalne kasyno mostbet mostbet casino
darmowe pobieranie mostbet mostbet
My husband and i have been quite satisfied Louis could carry out his research via the precious recommendations he was given through the web site. It is now and again perplexing just to choose to be releasing things which men and women might have been selling. And we also remember we have got the writer to thank for that. The specific explanations you made, the straightforward site navigation, the relationships your site help create – it is many unbelievable, and it is facilitating our son in addition to us know that the situation is exciting, which is certainly seriously fundamental. Many thanks for the whole thing!
You have remarked very interesting points! ps nice website .
выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал выпрямитель дайсон где купить оригинал .
Pingback: Off Grid Solar Systems: Key Difference, Advantage and Disadvantage