Define knee point voltage of a CT
When the primary of a Current transformer (CT) is open circuited and supply (variable) of system frequency is given to secondary, then a 10% increase in voltage constitutes 50%increase in current. That voltage is the knee point voltage. At this point the core is saturated and a little increase in voltage constitutes a great increase in current. kpv decides the opening range of the CT. Above kpv the ratio of transformer will not be applicable.
kpv = RCT + RLEADS + RRELAY
Procedure for find out the knee point voltage of Current Transformer
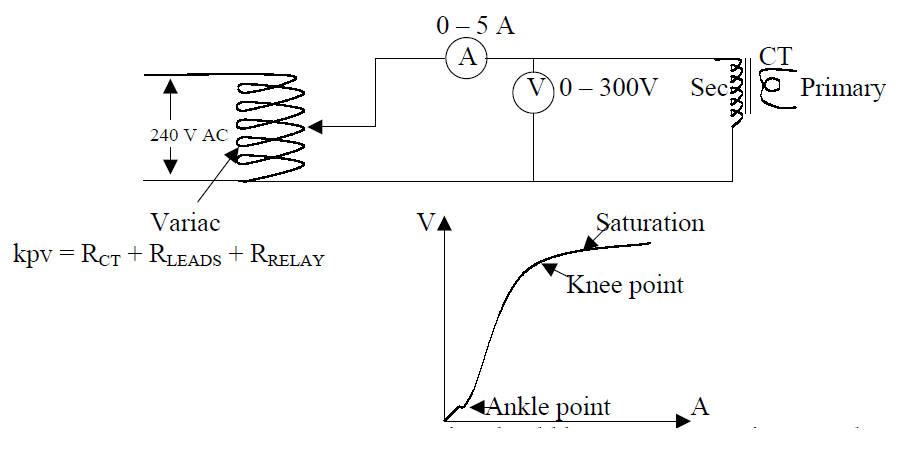
Connect the circuit as shown. O/P of variac should be zero. Increase it to 5Volts and take down the value of current from the ammeter. Now increase the voltage by 10%(5 + 10% = 5.5 V) and take the current reading. Now increase the voltage by 10%(5.5 V +0.55 V =6.05 V) and note down the current. Now keep on increasing voltage by 10% and note down current reading. At some value there will be 50% increase incurrent for 10% increase in voltage.
Example 40 V=0.2 A
40.4 V=0.3 A (0.2 + 50% = 0.3 A).
That point is the knee point voltage of that particular CT. From this point onwards a little increase in voltage will lead to a large increase in current, because the core is saturated fully. When we plot all the values on a graph taking current as X-axis and voltage as Y-axis, we will get the above graph. Protective relays operate between ankle point and knee point. Above this they cannot detect the fault correctly. Measuring CT operate in the ankle region.
