Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
In our ever-evolving world, where sustainable energy solutions are becoming increasingly essential, off grid solar systems have emerged as a beacon of hope. These systems, capable of harnessing the sun’s energy and converting it into usable electricity, offer an environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional power sources. However, like any complex technological setup, off-grid solar systems require vigilant monitoring and occasional troubleshooting to ensure they operate efficiently and effectively. This chapter delves into the crucial aspects of monitoring, diagnosing issues, and maintaining off-grid solar systems for prolonged and optimal performance.
Remote Monitoring and Data Analysis Tools
The Power of Remote Monitoring
Integrating remote monitoring technology has revolutionized how off-grid solar systems are managed. With remote monitoring, system owners and technicians can access real-time data and insights about the system’s performance without being physically present at the installation site. This capability significantly enhances system management efficiency and reduces the need for frequent on-site visits, which can be especially valuable for remote or inaccessible locations.
Data Analysis
Data holds the key to understanding the intricacies of any system’s performance, and off-grid solar systems are no exception. Remote monitoring systems continuously gather data points such as energy production, battery levels, and load consumption. Analyzing this data provides valuable insights into the system’s patterns, trends, and potential anomalies.
Solar systems generate electricity based on sun exposure, and their efficiency can be affected by factors such as shading, dust accumulation, or module degradation. Data analysis helps detect such issues promptly. For instance, if a sudden drop in energy production is detected, it could indicate a shading issue that needs to be addressed. By identifying such problems early, system owners can take corrective actions before they escalate into more significant complications.
Role of Remote Monitoring Tools
Various remote monitoring tools are available in the market, each offering unique features to cater to different needs. These tools typically include user-friendly interfaces accessible through web platforms or mobile applications. They provide a dashboard where users can visualize real-time data and historical trends and even receive alerts in case of system abnormalities.
Some advanced monitoring tools offer predictive analysis, using machine learning algorithms to forecast potential issues based on historical data and system parameters. This proactive approach empowers system owners to take preventive measures, minimizing downtime and maximizing energy production.
Troubleshooting Common Solar System Issues and Failures
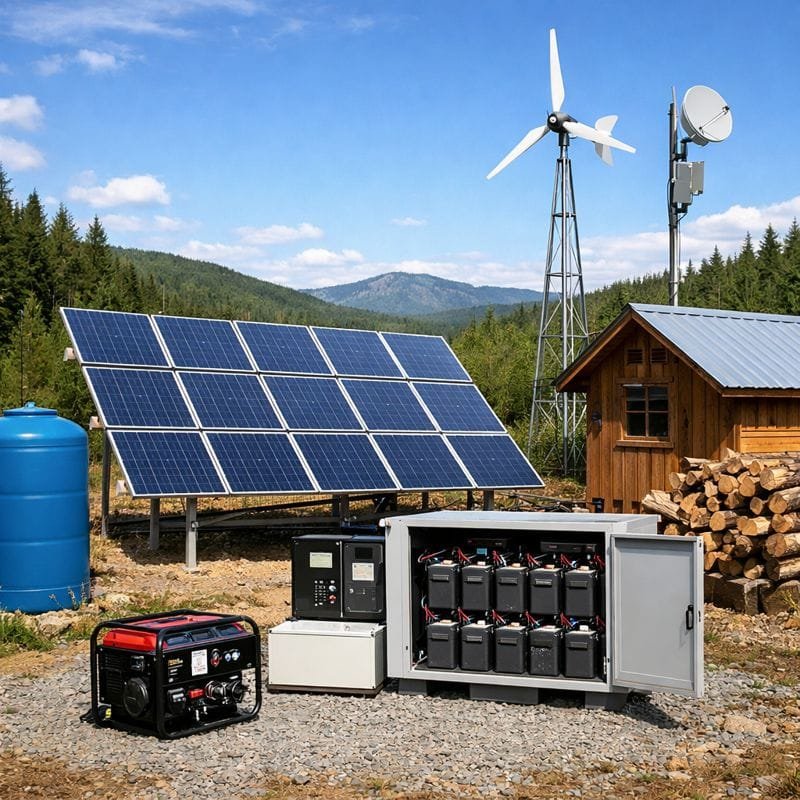
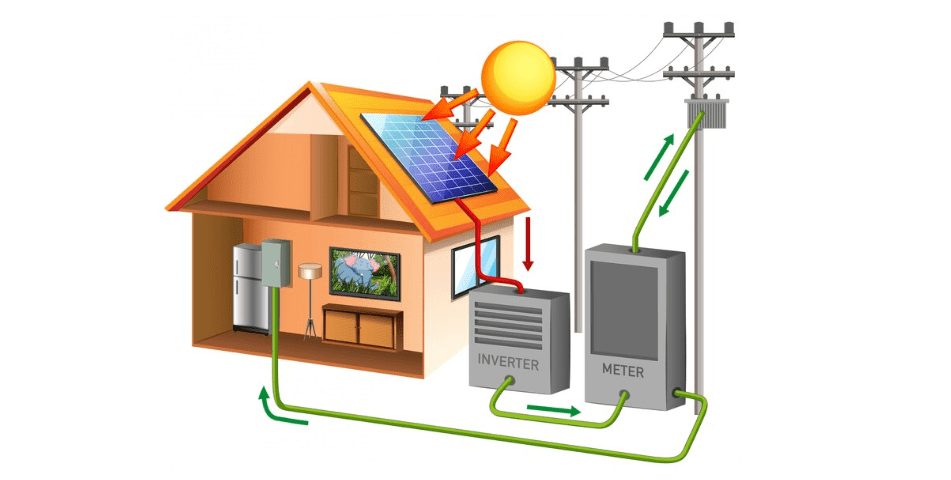
A fundamental prerequisite for effective troubleshooting is a comprehensive understanding of the different components that constitute an off-grid solar system. These components include solar panels, charge controllers, batteries, inverters, and the overall electrical wiring.
Solar panels are the heart of the system, responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. Charge controllers regulate the flow of energy from the panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging or deep discharging. Batteries store the generated energy for use during periods of low sunlight. Inverters convert the stored DC energy into AC, suitable for powering household appliances.
Off-grid solar systems can face issues ranging from minor glitches to critical failures. A systematic approach is essential to diagnose and resolve these problems effectively.
Energy Production Drop: If the system’s energy production decreases suddenly, it could indicate shading, dirt accumulation, or module malfunction. Visual inspection or using shade analysis tools can identify shading issues. Cleaning panels and replacing malfunctioning modules can restore energy output.
Battery Problems: Battery-related issues can lead to energy storage and supply problems. If batteries are not holding their charge or are overcharging, it might be due to faulty charge controllers or battery degradation. Voltage testing and assessing charge controller settings can help pinpoint the problem.
Inverter Failures: Inverters are crucial for converting energy into usable forms. A malfunctioning inverter can disrupt the entire system’s performance. Monitoring inverter logs and performing diagnostic tests can help determine whether the issue lies with the inverter itself or other components.
Wiring and Connection Faults: Faulty wiring and poor connections can result in power loss or electrical hazards. Regularly inspecting and maintaining the wiring infrastructure can prevent such issues. Using thermal imaging cameras can identify overheating connections.
Load Consumption Anomalies: Unexpected load spikes or irregular consumption patterns might point to appliance malfunctions or wiring issues within the household. Ensuring that appliances are in good working condition and assessing load distribution can address such problems.
Environmental Factors: Harsh weather conditions like extreme temperatures or heavy snow can impact system performance. Designing systems to withstand such conditions and implementing protective measures can mitigate their effects.
Maintenance of off grid solar system
Just like any mechanical system, off-grid solar systems require regular maintenance of solar system to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regularly cleaning solar panels is paramount to remove dirt, debris, bird droppings, or any other obstructions that can hinder sunlight absorption. Cleaning can be done using water, a soft brush, or specialized cleaning solutions.
Apart from cleaning, routine visual inspections should be conducted to identify signs of wear and tear, corrosion, loose connections, or physical damage. Early detection of such issues can prevent them from escalating and causing significant system disruptions.
Batteries are a crucial element of off-grid solar systems, and their proper maintenance is essential to prolong their lifespan. This involves checking battery voltage levels, specifically gravity, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent overheating. Regularly equalizing and topping up flooded lead acid batteries with distilled water can extend their operational life.
Inverters and charge controllers should be inspected for any unusual noises, heat emissions, or error codes. Regular firmware updates, if applicable, can enhance their performance and compatibility with other system components.
While some maintenance tasks can be carried out by system owners, engaging professionals for comprehensive system inspections is recommended at least once a year. These professionals can conduct in-depth assessments, perform electrical tests, and make any necessary adjustments to optimize the system’s efficiency.
Maintaining a detailed record of all maintenance activities, repairs, and component replacements is crucial. This documentation provides valuable insights into the system’s history, helping technicians identify recurring issues and track the system’s overall health.