Table of Contents
ToggleKey Differences between Off Grid Solar Systems and Grid-Tied Solar system
The fundamental distinction between grid-tied and off grid solar systems lies in their interaction with the electricity grid.
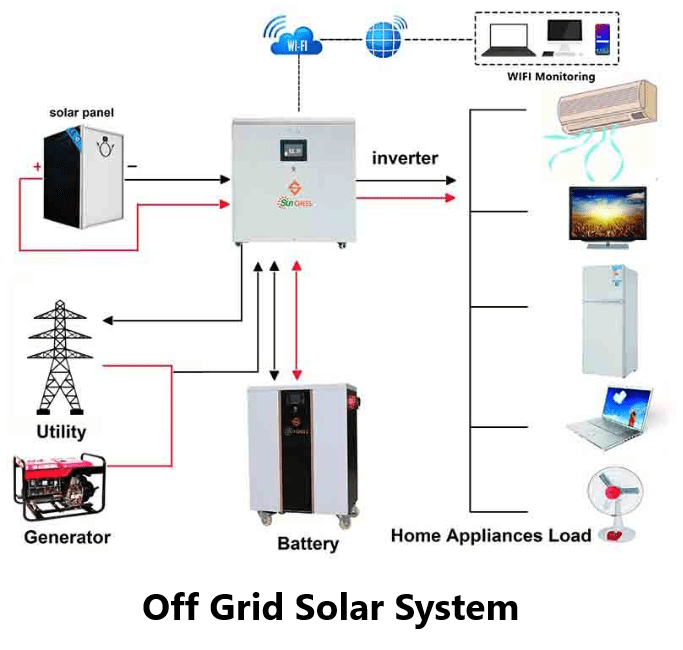
Off-grid solar systems operate independently of the utility grid. These systems are designed to provide all the energy required for a household or establishment without relying on external sources. Off-grid setups consist of solar panels, energy storage systems (typically batteries), charge controllers, inverters, and backup generators. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. Charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity to the batteries, preventing overcharging and prolonging their lifespan. Inverters convert DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is used to power household appliances. Energy storage in batteries ensures a continuous power supply during cloudy days or nighttime.
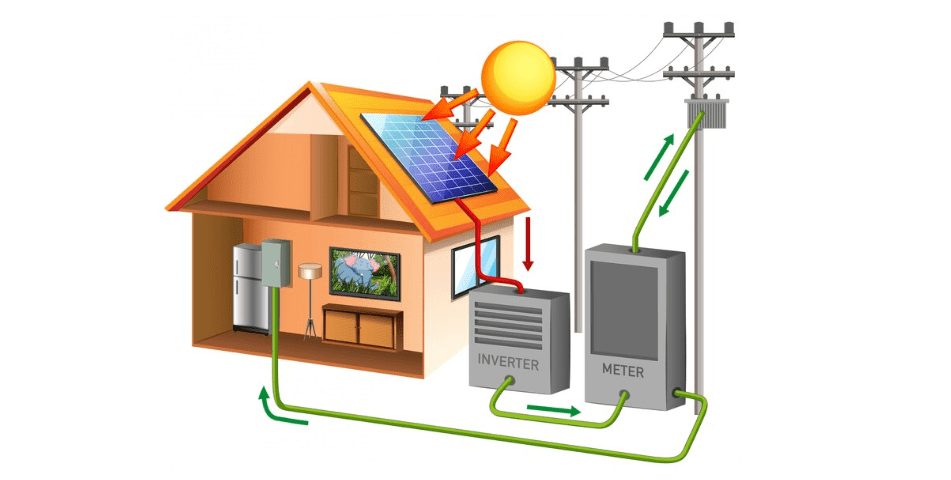
Grid-tied solar system is connected to the utility grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when their solar panels do not produce enough energy and to feed excess energy back into the grid when their panels generate surplus power. This interaction enables users to balance their energy consumption and potentially receive credits for the excess energy they contribute.
Choosing a grid-tied or off-grid system depends on several factors, including geographical location, energy consumption, budget, and personal preferences. Grid-tied systems are simpler to install and often more cost effective initially. They allow users to take advantage of net metering, reducing electricity bills by selling excess energy. However, these systems are vulnerable to grid failures, which means they won’t provide power during blackouts or emergencies. In contrast, off-grid systems offer energy independence and resilience, ensuring a consistent power supply regardless of grid status. Yet, they require a larger upfront investment due to the need for energy storage solutions.
Advantages of Off Grid Solar Systems
Energy independence, a hallmark of off-grid living, emerges as a compelling advantage, fostering an individual’s or community’s self reliance. Conventional energy sources like fossil fuels are finite, geopolitically sensitive, and contribute to environmental degradation. In contrast, off-grid systems predominantly rely on renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass, which are virtually inexhaustible and emit minimal greenhouse gases
From an environmental perspective, the off-grid approach exerts a significantly reduced carbon footprint. Traditional power generation methods, like coal-fired plants, emit pollutants that degrade air quality and contribute to climate change. By transitioning to off-grid systems, the emission of harmful gases and particulates is curtailed, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier ecosystem.
Energy Independence: One of the most appealing aspects of off grid solar power systems is the liberation from the uncertainties of the grid. Users are no longer subject to power outages, grid maintenance, or fluctuations in utility prices. This autonomy provides peace of mind and stability.
Environmental Benefits: Embracing off-grid solar power contributes significantly to reducing the carbon footprint. By generating clean energy from sunlight, users decrease reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions, thus actively participating in the fight against climate change.
Remote Accessibility: Off-grid systems are particularly advantageous in remote or rural areas where connecting to the grid might be expensive or logistically challenging. These systems empower communities that were previously underserved by traditional energy infrastructure.
Long-Term Savings: Although the initial investment for an off grid solar system can be substantial, it pays off over time. Users can recoup their costs through energy savings and potentially by selling excess power to others in the area.
Disadvantages of Off Grid Solar Systems
Higher Initial Costs: The upfront expenses of purchasing solar panels, batteries, inverters, and other components, along with installation and maintenance costs, can deter individuals from adopting off-grid systems, especially in comparison to grid-tied alternatives.
Complexity of Maintenance: Off-grid systems require regular monitoring and maintenance. Batteries need consistent attention to ensure optimal performance and longevity. In remote locations, accessing professional maintenance services can be challenging.
Limited Energy Storage: While advancements in battery technology have improved energy storage capabilities, off-grid systems still rely on the stored energy in batteries. Extended cloudy periods can potentially deplete stored energy, necessitating backup generators or reduced energy consumption.
Sizing Challenges: Properly sizing an off-grid system requires meticulous consideration of energy consumption patterns, weather conditions, and storage capacity. Undersized systems may lead to energy shortages, while oversized systems result in unnecessary expenses.
Application of Off grid solar system
Off grid solar power for small Homes:
Solar powered heating and cooling appliances, Solar water heater, Solar powered appliance and gadgets
Off grid solar system for boats or Ships:
Off grid solar system for Marine Solar, Solar Charge Controllers for Marine Environment, Solar-Powered Boat Refrigeration and Cooking, Solar-Powered GPS and Communication Devices, LED Navigation Lights and Solar Dock Lighting
Recent Trend in Off grid solar system
The integration of advanced solar panel technology and innovative energy storage solutions has ushered in a new era of off-grid solar power systems. These systems are no longer confined to remote cabins or research projects; they are becoming viable alternatives to traditional grid-connected setups in various settings.
Off-grid solar power systems are increasingly finding their way into residential settings. Homeowners are leveraging solar panels and energy storage solutions to become more self-reliant and reduce their dependence on traditional utility grids. This trend is particularly relevant in regions prone to power outages or those with limited access to reliable electricity sources.
In remote and underserved areas, off-grid solar power has emerged as a lifeline. Traditional grid infrastructure can be prohibitively expensive to establish in such regions. Off-grid solar power systems provide a cost effective and sustainable solution for bringing electricity to schools, healthcare facilities, and communities that have long been in the dark.
Natural disasters and humanitarian crises often disrupt essential services, including electricity supply. Off-grid solar power systems can be rapidly deployed to provide emergency energy sources for charging communication devices, running medical equipment, and maintaining basic living conditions in affected areas. Their portability and ease of installation make them indispensable tools in disaster relief efforts.
Industries and businesses are also recognizing the benefits of off-grid solar power. In remote mining operations, for instance, solar power can reduce reliance on costly diesel generators and decrease the environmental impact. Similarly, businesses seeking to align with sustainable practices can integrate off-grid solar power systems to power their operations while reducing their carbon footprint.


Pingback: Monitoring and troubleshooting Off grid solar system - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Battery Energy storage systems (BESS) - Electricalsphere
I discovered your blog site on google and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading more from you later on!…