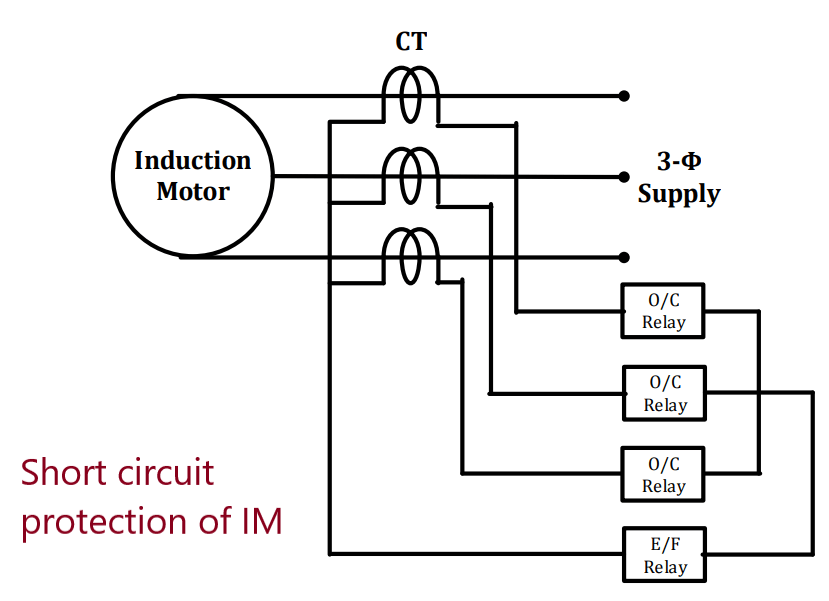
Short circuit protection of induction motor
Short circuit in induction motor occurs either due to winding insulation failure or blocking of rotor. Winding insulation failure takes place because of phase faults and rotor does not start rotating i.e. blocked due to heavy load or bearing failure.
Motor draws a heavy short circuit current that produces high electrodynamic force enough to destruct motor. An instantaneous overcurrent relay with pickup a little above the maximum starting current is capable to isolate the motor from supply within 3 cycles.
Generally pickup of relay is selected as starting current at 75% of the rated voltage. Overcurrent relay characteristics should be lower than thermal withstand characteristics of the motor.
Earth fault current of induction motor is difficult to detect by over current relay as its magnitude is less than full load current of motor. Hence three over current and one earth fault protection scheme is implemented for short circuit protection of induction motor.
Interturn fault in any phase does not cause any change in current drawn by motor, hence it is difficult to detect. Such fault creates hot spot at the location of interturn short circuit. Embedded resistance temperature detector (RTD) helps to provide protection against interturn fault.
High impedance earth fault is detected through earth leakage differential protection. In this protection all three phase conductors are threaded through core balance CT.
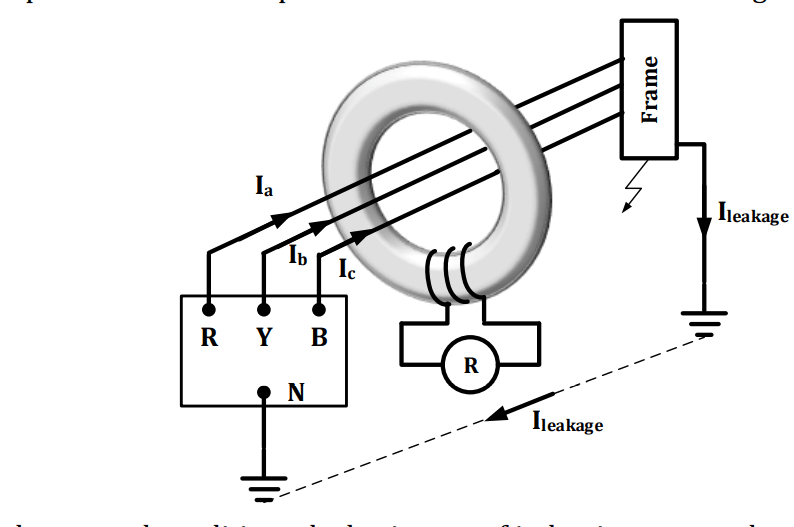
Under normal condition, algebraic sum of induction motor phase current is zero. Hence flux produced by three phase current is zero i.e. no net flux in core. Consequently flux linkage with relay pickup coil is zero i.e. emf induced in coil is also zero that keeps relay inoperative.
Under faulty condition, algebraic sum of induction phase current is non zero and gets divided in two part, one current returns through supply neutral conductor and second returns through earth. Hence a differential flux sets up in toroidal core links with relay pick up coil and induces the emf in coil that operates the relay.
Protection against single phasing of induction motor
When connect of any one supply phase gets open due to improper connection of excessive heating, induction motor continue to run but current drawn by other phase is increased.Unbalanced stator current due to single phasing contains negative sequence component of current that causes excessive iron loss and heating of rotor core.
As motor over current is time delayed operation to match with overload profile of motor, it is not able to protect induction motor against single phasing.
Large motors are provided with separate single phase protection while for small motors thermal overload real does the duty.
Increased CT secondary current due to single phasing, gives tripping command to motor starter circuit or negative sequence component of current gives the tripping command to circuit breaker.
