Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Solar collector?
Sun’s heat energy is a diffuse energy. It is always first collected and then concentrated. In residential systems, simple and cheap solar panels are used to collect the solar heat energy below 60°C. Residential panels for heat collection are referred to as flat plate collectors. Solar energy collectors are special kind of heat exchangers that transform solar radiation energy into internal energy of the transport medium. The major component of any solar system is the solar collector.
Types of Solar collector
To utilize thermal energy from the sun, the collectors can be subdivided into following categories, they are
Non Concentrating collectors:-(i) Flat plate collector (a) Flat plate air collector (b) Flat plate liquid collector (ii) Evacuated tube collector
Concentrating collectors:-(a) Stationary Concentrating collectors (b) Tracking Concentrating collectors (c) Parabolic dish collector (d) Heliostat field collector (e) Parabolic Trough collector
What is Flat plate collector?
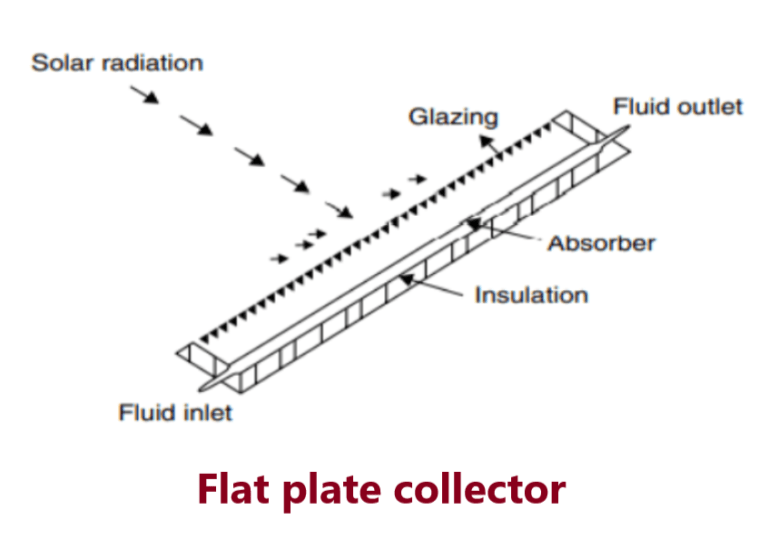
Flat plate collectors are the most common type. They are also referred to as non concentrating collectors and have the same area for intercepting and for absorbing solar radiation.
A typical flat plate collector is an insulated metal box with a glass or plastic cover (called the glazing) and a dark-coloured absorber plate.
These collectors heat liquid or air at temperatures less than 90°C. Flat plate collectors are used for residential water heating and space heating installations.
Components
It has five essential parts as per below mention:
- Dark flat plate absorber of solar energy: The absorber consists of a thin absorber sheet (of thermally stable polymeric materials such as aluminium, steel, or copper to which a black or selective coating is applied) because of the fact that the metal is a good heat conductor. Copper is more expensive, but is a better conductor and less prone to corrosion than aluminium
- Transparent cover: This allows solar energy to pass through, but reduces heat losses.
- Heat-transport fluid (air, antifreeze, or water): To remove heat from the absorber, fluid is usually circulated through tubing to transfer heat from the absorber to an insulated water tank.
- Heat insulation backing: Often backed by a grid or coil of fluid tubing.
- Insulated casing: It is made of a glass or polycarbonate cover.
What is Flat plate air Solar collector?
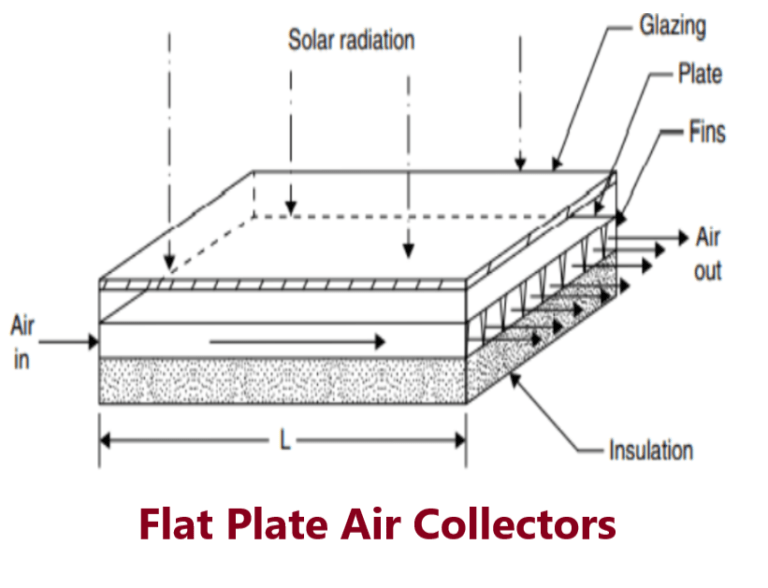
It uses air as the heat transport medium. Air flat plate solar collectors are used mainly for solar space heating. The absorber plates can be made of metal sheets, layers of screen, or non-metallic materials. The air flows past the absorber by using natural convection or a fan. Since air does not conduct heat as easily as liquid, air collectors are typically less efficient than liquid collectors.
What is Flat plate liquid solar collector?
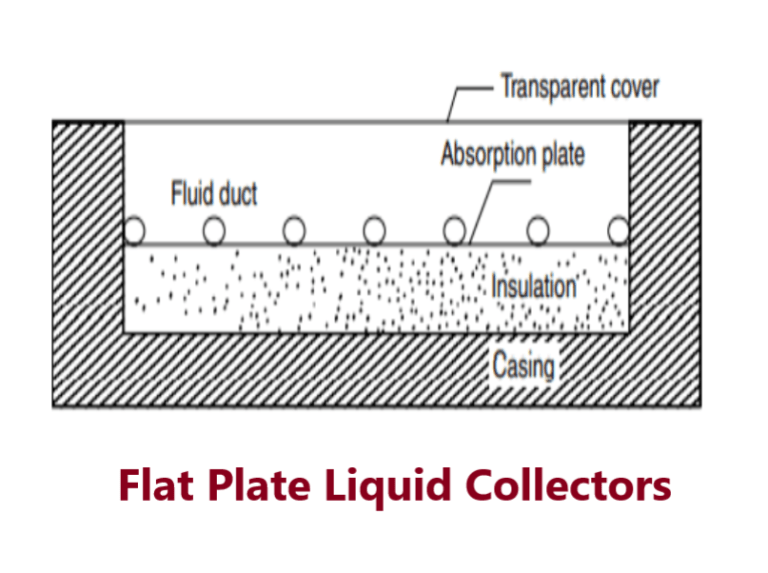
These solar collectors use liquid as the heat transport medium. Liquid flat plate collectors heat liquid as it flows through tubes in or adjacent to the absorber plate as shown in Figure. The simplest liquid systems use household water that is heated as it passes directly through the solar collector and then flows to the house.Solar pool heating uses liquid flat plate technology, but the collectors are typically unglazed. The liquid tubes can be welded to the absorbing plate, or they can be an integral part of the plate.
The most common air and liquid-based solar thermal solar collectors are as follows:
- Glazed flat plate solar thermal collectors
- Unglazed flat plate solar thermal collectors
- Unglazed perforated flat plate solar thermal collectors
- Back-pass flat plate solar thermal collectors
- Batch flat plate solar thermal collectors 6. Solar cookers
- Evacuated (vacuum tube) flat plate solar thermal collectors
- Concentrating (flat plate collectors with flat reflectors)
Evacuated Tube solar Collectors
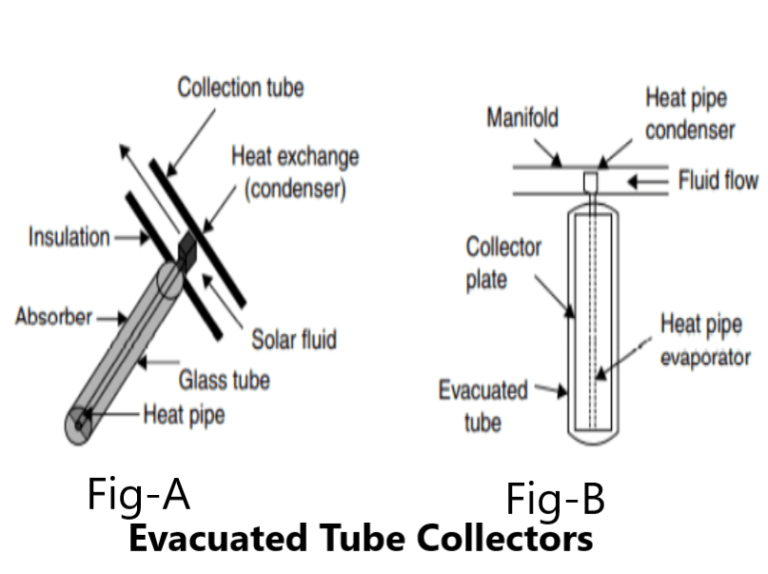
Evacuated heat pipe solar collectors (tubes) operate differently than the other collectors available on the market. These solar collectors consist of a heat pipe inside a vacuum-sealed tube, as shown in Fig A and Fig B.
Evacuated tube collectors can achieve extremely high temperatures (75°C–180°C), making them more appropriate for cooling applications and for commercial and industrial applications. Evacuated tube collectors are more expensive than flat plate collectors, as their unit area costs about twice than that of the latter.
These collectors are best suited for moderate temperature applications where the demand temperature is 50–95°C Applications of vacuum tube collectors include heating of domestic and commercial hot water, buildings, and indoor swimming pools. Ted tube collectors are efficient at high temperatures.
Concentrating solar Collectors
It is used for high-temperature applications such as steam production for the generation of electricity and thermal detoxification. These collectors are best suited to climates that have an abundance of clear sky days, and therefore. Concentrating collectors are of various types and can be classified in many ways.
They may be as follows:
- Based on means of concentration: reflecting type use mirrors or refracting type use Fresnel lenses.
- Based on reflecting surfaces used: parabolic, spherical, or flat.
- Continuous or segmented.
- Based on the formation of the image: imaging or non-imaging.
- Imaging concentrator may focus on a line or at a point.
- On the basis of collector concentration ratio or operating temperature range.
- By the type of tracking.
Material aspects of solar collectors
Absorber
The following are the types of solar flat plate absorbers that are most frequently used
- all copper plates are with integrated water passage (roll bond type). These plates can also be made of aluminium.
- all copper (copper tube on copper sheet).
- copper tube or aluminium fin
- iron or steel
- plastic (polymers)
Specification requirement of an absorber coating for a flat plate collector is as follows:
- It must not degrade under ultraviolet exposure.
- It must withstand temperature up to 200° C.
- It must withstand many temperature cycles over ±40° C.
- It must withstand many cycles of low to high relative humidity.
- It must not chalk, fade, or chip.
- It must not be so thick that heat conduction through the paint to the metal absorber is impeded.
Glazing
- Glass and fibreglass
- Tedlar when bonded to the fibre glass, it acts as a good glazing material.
- Optical rating must not change during its service life.
- Glazing material must be resistant to UV radiation
- Plastic radiation can easily withstand for temperature shock
Insulation Shell
A solar flat plate collector must be insulated against excessive heat losses on its back side and on its edges as follows:
- Back side – 3.5 inch of fiberglass insulation or 2 inch of foam insulation.
- Side – 1 inch of fiberglass or 0.5 to 0.75 inch of foam insulation
Video Tutorial-Flat Plate Solar collector
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
1. What is a solar thermal collector?
A solar thermal collector is a device designed to capture sunlight and convert it into heat energy. It typically consists of a flat plate or tubes containing a heat-absorbing material, such as metal or glass, which heats up when exposed to sunlight.
2. How does a solar thermal collector work?
Solar thermal collectors work on the principle of converting sunlight into heat energy. The collector absorbs sunlight using a heat-absorbing material, which then heats up and transfers the heat to a fluid circulating within the collector. This heated fluid can then be used directly for space heating, water heating, or to generate electricity through a heat engine.
3. What are the types of solar thermal collectors?
There are several types of solar thermal collectors, including flat-plate collectors, evacuated tube collectors, concentrating collectors, and integrated collector-storage systems. Each type has its own advantages and applications depending on factors such as efficiency, cost, and intended use.
4. What are the applications of solar thermal collectors?
Solar thermal collectors can be used for various applications, including domestic water heating, space heating, pool heating, industrial process heating, and electricity generation through concentrated solar power (CSP) systems.
5. What are the benefits of using solar thermal collectors?
The benefits of using solar thermal collectors include reduced energy bills, decreased reliance on fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional energy sources. Solar thermal systems also have low operating and maintenance costs and can provide energy independence to users.
6. Are there any limitations to using solar thermal collectors?
While solar thermal collectors offer many benefits, they also have some limitations. They are dependent on sunlight and may not be suitable for areas with limited sunlight or frequent cloud cover. Additionally, the initial cost of installation can be high, although this is often offset by long-term energy savings.
7. How do I maintain a solar thermal collector system?
Maintaining a solar thermal collector system typically involves periodic inspections, cleaning the collector surface, checking fluid levels and pressure, and ensuring that all components are functioning properly. It’s also important to protect the system from freezing temperatures if it is used for water heating.
8. Are there any incentives or subsidies available for installing solar thermal collectors?
Many governments and utilities offer incentives, rebates, tax credits, or other financial incentives to encourage the installation of solar thermal collector systems. These incentives can help offset the initial cost of installation and make solar thermal technology more affordable for homeowners and businesses.
9. How long do solar thermal collector systems last?
With proper maintenance, solar thermal collector systems can last for 20-30 years or more. The lifespan of the system may vary depending on factors such as the quality of components, installation, and environmental conditions.
10. Can solar thermal collectors be integrated with existing heating systems?
Yes, solar thermal collectors can often be integrated with existing heating systems, such as boilers or radiant floor heating systems. This can help supplement traditional heating sources and further reduce energy costs and environmental impact.


I go too see daqily some sites and sites to read articles,
but this web site gives quality based content. https://Www.Waste-Ndc.pro/community/profile/tressa79906983/
I go tto see daily some sites and sitds to read
articles, but this web sitfe gives quality based content. https://Www.Waste-Ndc.pro/community/profile/tressa79906983/
Wow! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a entirely different subject but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Outstanding choice of colors!
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your website in Firefox, it looks fine
but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that,
amazing blog! https://in.norton.com/blog/how-to/what-is-cryptocurrency-and-how-does-it-work https://in.norton.com/blog/how-to/what-is-cryptocurrency-and-how-does-it-work
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your website in Firefox, it looks fine
but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping.
I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, amazing blog!
https://in.norton.com/blog/how-to/what-is-cryptocurrency-and-how-does-it-work https://in.norton.com/blog/how-to/what-is-cryptocurrency-and-how-does-it-work
Thanks for every other magnificent article. Where else may
anyone get that type of information in such an ideal method of writing?
I’ve a presentation next week, and I am at the look for such information. https://wakelet.com/wake/_8VsKQGlERFosVABHwfxC
Thanks for every other magnificent article. Where else may anyone get that type of information in such an ideal method of
writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am at the look for such information. https://wakelet.com/wake/_8VsKQGlERFosVABHwfxC
Thank you for this interesting article! Very useful information.
Verification: VRF637DC076
Impressive write-up
Pingback: Monitoring and troubleshooting Off grid solar system - Electricalsphere