Table of Contents
ToggleSolar plant system components
The four major components of a solar energy system are the panels, inverter, racking and solar battery storage unit.
Solar Panel
Solar panels are the most visible element of your system, which is why you’re likely the most familiar with it. The way that solar panels work is that the panels generate DC electricity as sunlight, or solar irradiation, stimulates electrons to move though solar cells that are in-built into the solar panels.
Monocrystalline panels consist of singular large crystals, are darker in colour, even in aesthetic consistency and, as a result of the production process, the corners of cells are usually missing.
Polycrystalline panels consist of multiple smaller crystals, can be light or dark blue in colour and have variation in texture where some patches are lighter than others.
Inverters
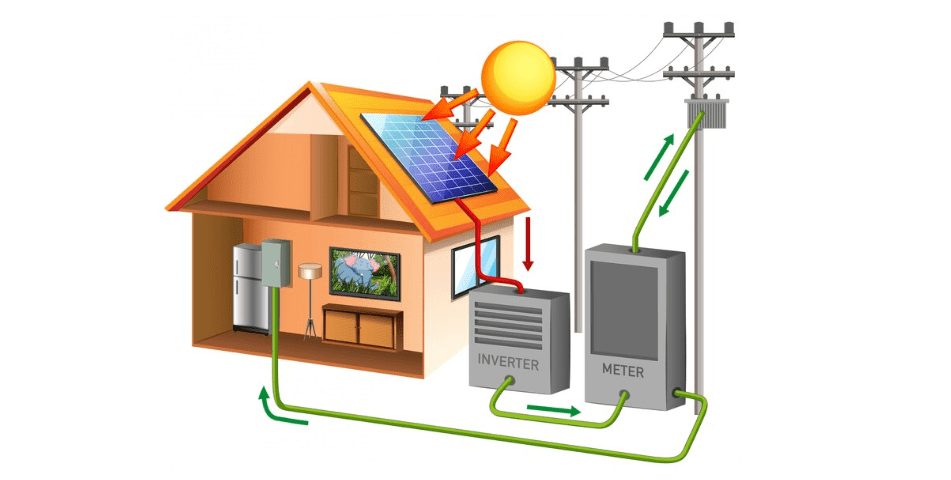
Inverters are a crucial part of any solar energy system. Their purpose is to convert the DC electricity that the solar panels produce into 240V AC electricity, which is what powers everything in your home. The inverter is a hardworking piece of equipment that works constantly throughout the lifetime of your system – so it tends to be the piece most likely to have faults.
Racking
The third main component of a solar energy system is the racking/mounting. This is what securely attaches your panels to your roof. Racking / mounting will not be a decision you need to lose sleep over. Any reputable solar provider will use quality racking equipment from brands like Radiant or Sunlock, which are Australian made.
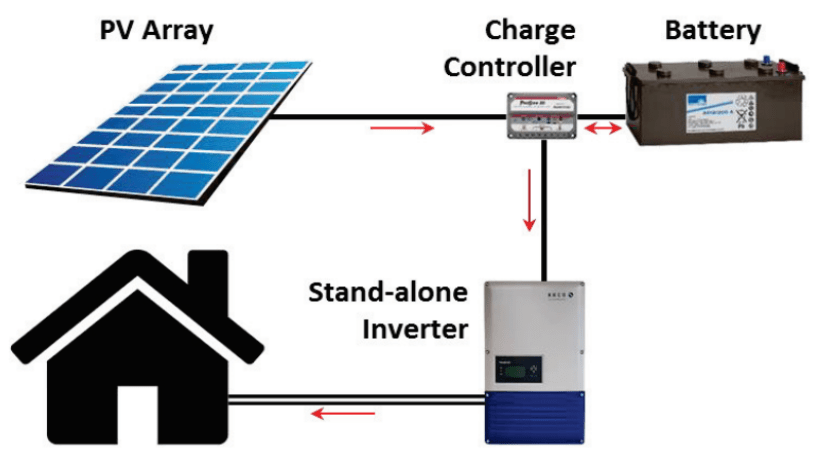
Batteries are used to store energy generated during the day to be used throughout the night when the system is no longer generating power. Battery technology is quickly developing into a more feasible option for those who primarily use their energy in the evenings. We have installed battery systems for major clients such as PCYC Queensland and schools like Bundaberg Christian College, who operate sporting facilities and boarding colleges that require energy throughout the night.
Charge controller
A charge controller is an important component in a battery based solar system and are not used in straight grid tie systems. The primary role is to manage charging the battery bank, prevent it from overcharging and many control the rate of the current and voltage at which it charges.
Series and Parallel Connection in Solar system
Series Wiring:Series wiring is when the voltage of a solar array is increased by wiring the positive of one solar module to the negative of another solar module. This is similar to installing batteries in a flashlight. As you slide the batteries into the flashlight tube the voltage increases.
Parallel Wiring:Parallel wiring increases the current (amps) output of a solar array while keeping the voltage the same. Parallel wiring is when the positives of multiple modules are connected together and all the negatives for the same modules are connected together.
Series Parallel Combination:Here is an example of what is found in most large solar systems, a series and parallel wiring combination.
Pole mounting for Solar panel installation
Photovoltaic mounting systems (also called solar module racking) are used to fix solar panels on surfaces like roofs, building facades, or the ground. These mounting systems generally enable retrofitting of solar panels on roofs or as part of the structure of the building (called BIPV).
Angle of tilt for Solar Panel:- The “tilt angle” or “elevation angle” describes the vertical angle of your solar panels. “Azimuth angle” is their horizontal facing in relation to the Equator. Solar panels should face directly into the sun to optimize their output.
The optimum tilt angle is calculated by adding 15 degrees to your latitude during winter, and subtracting 15 degrees from your latitude during summer. For instance, if your latitude is 34°, the optimum tilt angle for your solar panels during winter will be 34 + 15 = 49°.
Placement of solar panel mounting
The most optimum direction to face your solar panels is somewhere between south and west. It is at this location that your panels will receive the maximum sunlight throughout the day. If your roof does not face the right direction, then surface mounted panels or pole mounted panels may be your best bet.
Site Surveying Method
Roof Orientation and Shading Analysis- Helpful in in identifying the suitable location for Solar Panel installation.
Roofing Details – Study the roofing details to install the right solar PV system.
Load Analysis – Helpful to understand the energy needs of the building.
Evaluation parameters for Solar system
The following are the parameters you should evaluate on:
Grade – Solar panels come in Grades A, B & C (Grade A being the highest quality)
Tier of the manufacturer – Organizations such as BNEF have come up with ranking of the solar panel manufacturer, classifying them into one of three Tiers (Tier 1 being the highest)
Efficiency – Solar panels have efficiencies ranging from 13%-24%
Performance under low light conditions – Some solar panels can generate higher amounts of electricity than other panels with the same
Temperature coefficient – Solar panels with lower temperature coefficient (and higher temperature tolerance) lose less of their efficiency at higher temperatures
Warranties available – Solar panels come with performance warranties, which range from Standard to Linear
Presence of anti-PID features – Solar panels also come with features to tackle PID or Potential Induced Degradation, a characteristic that can cause significant harm to the panel within the first few years of installation.


Pingback: What is Solar Inverter and Types of Solar Inverter
Pingback: Role of Electrical Engineer in Construction - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Why electrician is good carrier in USA - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Electricity use in crypto mining - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Batteries in Solar System and Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Solar Energy generation impact on Power Grid
Pingback: Off Grid Solar Systems: Key Difference, Advantage and Disadvantage
Pingback: Hybrid Solar power System