Table of Contents
ToggleMethod of Underground Cable laying
Laying Underground Cables can be done by the 3 methods namely:
Direct Laying
Draw in system
Solid system
Direct Underground cable laying

This method of laying underground cables is simple and cheap and is much favored in modern practice. In this method, a trench of about 1·5 meters deep and 45 cm wide is dug. The trench is covered with a layer of fine sand (of about 10 cm thickness) and the cable is laid over this sand bed.
The sand prevents the entry of moisture from the ground and thus protects the cable from decay. After the cable has been laid in the trench, it is covered with another layer of sand of about 10 cm thickness. The trench is then covered with bricks and other materials in order to protect the cable from mechanical injury.
When more than one cable is to be laid in the same trench, a horizontal or vertical inter-axial spacing of at least 30 cm is provided in order to reduce the effect of mutual heating and also to ensure that a fault occurring on one cable does not damage the adjacent cable. Cables to be laid in this way must have serving of bituminized paper and hessian tape so as to provide protection against corrosion and electrolysis.
Advantages of Direct Laying
It is a simple and less costly method.
It gives the best conditions for dissipating the heat generated in the cables.
It is a clean and safe method as the cable is invisible and free from external disturbances.
Disadvantages of Direct Laying
The extension of load is possible only by a completely new excavation which may cost as much as the original work.
The alterations in the cable network cannot be made easily.
The maintenance cost is very high.
Localization of fault is difficult.
It cannot be used in congested areas where excavation is expensive and inconvenient.
This method of laying cables is used in open areas where excavation can be done conveniently and at low cost.
Draw-in system of Underground cable laying

In this method, conduit or duct of glazed stone or cast iron or concrete are laid in the ground with manholes at suitable positions along the cable route. The cables are then pulled into position from manholes. Figure shows section through four-way underground duct line. Three of the ducts carry transmission cables and the fourth duct carries relay protection connection, pilot wires. C
are must be taken that where the duct line changes direction, depths, dips and offsets be made with a very long radius or it will be difficult to pull a large cable between the manholes. The distance between the manholes should not be too long so as to simplify the pulling in of the cables. The cables to be laid in this way need not be armored but must be provided with serving of hessian and jute in order to protect them when being pulled into the ducts.
Advantages
Repairs, alterations or additions to the cable network can be made without opening the ground.
As the cables are not armored, therefore, joints become simpler and maintenance cost is reduced considerably.
There are very less chances of fault occurrence due to strong mechanical protection provided by the system.
Disadvantages
The initial cost is very high.
The current carrying capacity of the cables is reduced due to the close grouping of cables and unfavorable conditions for dissipation of heat.
Solid system of Underground cable laying
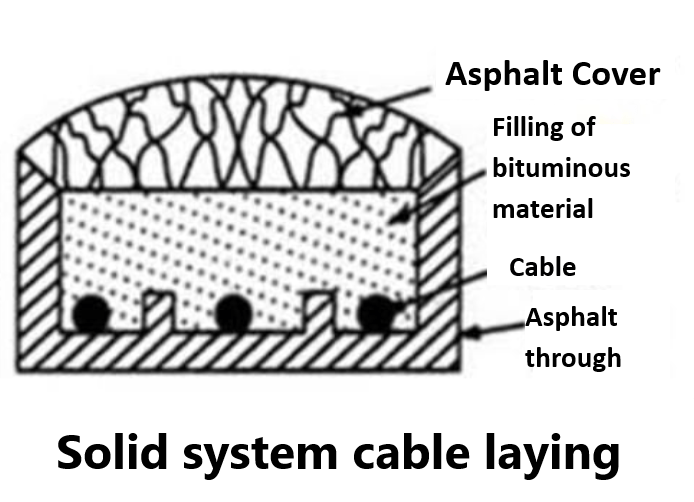
In this method of laying, the cable is laid in open pipes or troughs dug out in earth along the cable route. The toughing is of cast iron, stoneware, asphalt or treated wood. After the cable is laid in position, the toughing is filled with a bituminous or asphaltic compound and covered over. Cables laid in this manner are usually plain lead covered because toughing affords good mechanical protection.
Disadvantages
It is more expensive than direct laid system.
It requires skilled labor and favorable weather conditions.
Due to poor heat dissipation facilities, the current carrying capacity of the cable is reduced. In view of these disadvantages, this method of laying underground cables is rarely used now-a days.


Pingback: Underground Cable: Their types, Rating, insulation material, advantages - Electricalsphere
Pingback: XLPE cable: Construction, Voltage rating, Advantage
Much love and thanks! ✨
My goal is to provide accurate and usefull information to all the readers.
Please share my content to your group friends.This is really encouraging my website.
Thanks for appreciation.