Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
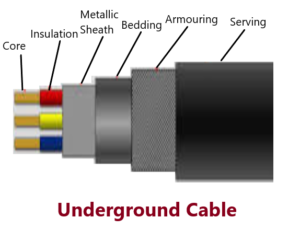
Since the loads having the trends towards growing density. This requires the better appearance, rugged construction, greater service reliability and increased safety. An underground cable essentially consists of one or more conductors covered with suitable insulation and surrounded by a protecting cover.
The interference from external disturbances like storms, lightening, ice, trees etc. should be reduced to achieve trouble free service. The cables may be buried directly in the ground, or may be installed in ducts buried in the ground.
Classification of Underground Cable
Things may be classified on many aspects and similar is the case with cables. There are several ways of classifying cables. These includes classification of cables on the basis of
No. of Conductors in Cable
Voltage Rating of Cable
Insulation Used in Cable
Power To Be handled in Cable
No. of Conductors in Cable
On the basis of number of conductors in the cable, cables are of two types viz Single core cables and 3 core cables. Single core cable have only one conductors and the diagram is shown in Underground Cable Basics while three core cable has three conductors and they have bedding and filler too. so on the basis of number of conductors cables are of two types 1. Single Core Cable 2. 3 Core Cable
Voltage Rating of Cable
Cables may be classified on the basis of voltage rating also
LT Cables : Cables up to 1000 Volts or l kV are called LT (Low Tension) or LV (Low Voltage) cables
HT Cables : Cables from 1001 volts to 11000 Volts or 11kV are called HT (High Tension) or HV (High Voltage) cables.
ST Cables : Cables from 11001 volts to 33000 Volts or 33kV are called ST (Super Tension) cables.
EHV Cables : Cables from 33001 volts to 66000 Volts or 66kV are called EHT (Extra High Tension) or EHV
Oil & Gas Filled Cables : From 66 kV to 132 kv Oil and Gas Filled cables are used.
EST Cables : Cables used above 132 W are called EST (Extra Super Tension) cables.
Insulation Used in Cable
Cables are also classified on the basis of insulation provided in the cable. Following are the type of cables on the basis of insulation used in the cable.
PIC or PILC : Paper Insulated Cable – Paper is used as insulation to the conductor.
PVC : Poly Vinyle Chloride Cable – PVC is used as insulation to the conductor.
PE : Poly Ethylene – Poly Ethylene is used as insulation to the conductor
PTFE : Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene – PTFE is used as insulation to the conductor
XLPE : Cross Linked Poly Ethylene – Cross Linked Poly Ethylene is used as insulation. This is most commonly used cable in Industry.
Power to Be handled in Cable
On the basis of amount of power to be transferred through the cable. cables are classified into two categories. These are
Power Cables : If large amount of power is to be transferred then these are called power cables. These are further classified on the basis of voltage at which power is to be delivered.
Low Voltage Power Cable : If the voltage in the cable is less then 1000 Volts or I kV then the cable is called Low Voltage Power Cable.
High Voltage Power Cable : If the voltage in the cable is above 1000 Volts or l kV then the cable is called High Voltage Power Cable.
Insulating materials used in Underground cables
The insulating materials used in underground cables are.
- Rubber
- VIR
- Impregnated paper
- PVC
- Varnished cambric
Rubber
It is the most commonly used insulating material. Natural rubber is produced from the latex of the rubber tree. Synthetic rubber is produced from alcohol or oil products. It absorbs moisture slightly and is soft. Therefore pure rubber cannot be used as an insulating material.
Vulcanized India Rubber (VIR)
It is used for low voltage power distribution systems only. It is prepaired by mixing pure rubber with mineral matter such as sulphur, zink oxide, red lead etc. it has greater mechanical strength than pure rubber. The advantages of using this type of rubber for cable is that, the cable becomes strong and more curable before using VIR as insulation, the copper conductor must be tunnel well because it attacks copper. (Reacts copper) its use is limited because of its low melting point and short span of life.
Impregnated Paper
It has low capacitance, high dielectric strength and economical. The paper is manufactured with wood pulp, rags or plant fiber by a suitable chemical process. It has high resistance due to high resistivity center dry condition. It absorbs a small amount of moisture only, which reduced the insulation resistance. For this drawback it requires some sort of protective covering. It is impregnated in insulating oil before used.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
It is a synthetic compound material. It is obtained from the polymerization of acetylene and is in the form of white power. It is combined chemically with a plastic compound and is used over the conductor as an insulation cover. It has high insulation resistance, good dielectric strength.PVC insulated cables are usually employed for medium and low voltage domestic insulation.
Varnished Cambric
It is the cotton cloth impregnated and coated with varnish. The cambric is lapped on the conductor in the form of a tape and its surface are coated with petroleum jelly compound to allow for the sliding of one turn over another as the cable is bent.
Advantages and Disadvantages of underground cable
Advantages
Better general appearance
Less liable to damage through storms or lighting
Low maintenance cost» Less chances of faults
Small voltage drops
Disadvantages
The major drawback is that they have greater installation cost and introduce insulation» problems at high voltages compared with equivalent overhead system.


Pingback: XLPE cable: Construction, Voltage rating, Advantage
Pingback: How to locate Cable fault - Electricalsphere
My spouse and i were quite thrilled when John could carry out his inquiry with the ideas he made through your blog. It is now and again perplexing to simply continually be freely giving secrets and techniques which a number of people might have been trying to sell. And we also recognize we now have the website owner to appreciate for this. These explanations you’ve made, the easy website navigation, the relationships you give support to create – it’s got many astounding, and it is aiding our son and our family know that this issue is entertaining, and that’s particularly pressing. Many thanks for all!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.