Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
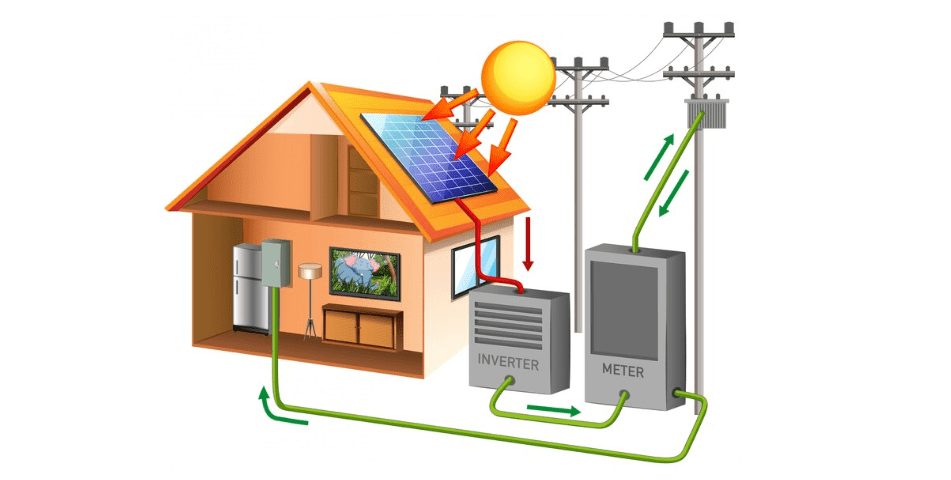
The number of solar power installations around the country is growing faster each year, creating an ever-increasing demand for technicians who know how to troubleshoot photovoltaic (PV) systems efficiently and effectively. Troubleshooting a PV system will typically focus on four parts of the system: the PV panels, load, inverter, and combiner boxes.
Troubleshooting Solar power panels
First check the output of the entire system at the metering system or inverter. Before you begin troubleshooting, check and record the inverter’s input voltage and current level from the array. You will likely encounter one of two scenarios:
The entire PV system, or a portion of it, is down or not producing power; this may be related to a problem with the inverter. Or the PV system output is less than expected; this may be related to a problem with one of the arrays or modules.
Trace out the individual branch wiring backward from the concentrator. Check the entire system visually for any obvious damage or accidental disconnections. Once you find the failed module or array, check all wires, switches, fuses, and circuit breakers. Replace blown fuses; reset the breakers and switches. Check for broken wires and loose or dirty connections; replace and clean as needed. Be on the lookout for loose connections between the modules. They may have worked loose and caused lack of contact.
The combiner box can be a great place to troubleshoot the system because the individual wires from the modules are brought back to it. Each module may have a fuse that you should check with digital multi meter.
Wiring problems and loose connections may also cause a module to produce too low a voltage. Check all wiring connections. If a module output is low, it may mean that an individual section of cells is bad. These can be traced out using the digital multimeterat the junction boxes until the culprit is found.
The digital multimeterprovides an audio polarity warning when you’re testing Voc. If you find that polarity is reversed, it may mean that other circuits in the combiner box are unintentionally connected in series, resulting in voltages over the maximum inverter input voltage.
Any dirt or shade on the modules themselves can cause reduced output. Although the modules are usually designed to be maintenance free for years, they may need to be cleaned. Pollen and dust can be a significant problem in some areas of the country.
Troubleshooting Solar power loads
The PV system is used to operate building electrical loads; any problems with the loads will affect the system as well. The first step is to check the load switches, fuses and breakers with the digital multi meter to see if the proper voltage is present at the load’s connection. Next, use the digital multi meter to check the fuses and circuit breakers. If you find blown fuses or tripped breakers, locate the cause and fix or replace the faulty component. If the load is a motor, an internal thermal breaker might be tripped or there might be an open winding in the motor. For testing purposes, plug in another load and see if it operates properly.
As with any electrical system, check for broken wires and any loose connections. Clean all dirty connections and replace all bad wiring. With the power off, check for and repair any ground faults. If any fuses or breakers blow or trip again, there’s a short that you need to locate and repair.
If the load still does not operate properly, use the digital meter to check the system’s voltage at the load’s connection. The wire size may be too small and need to be increased. It may also be possible that that the wires running to the loads are too long. This will show up as a low voltage at the load. In this case you can reduce the load on the circuit or run a larger wire.
Troubleshooting Solar Power inverters
You likely work with variable speed drives every day, so are used to checking ac and dc power. The inverter in a PV system can also fail and cause problems. The inverter converts dc from the PV system into ac power for building use.
If the inverter isn’t producing the correct output, first use check and record the inverter’s operating dc input voltage and current level. On the ac side, use the digital multi meter to check the inverter’s output voltage and current levels. Many of these systems have a display that indicates current inverter and system performance. Because the digital multi meter produces a true-rms reading, you can use the voltage and current to measure and record the kilowatt (kW) output. If possible, use the inverter display to show the current total kilowatt hours (kWh).
You can then write down this value and compare it to the one recorded during the last inspection. On the dc side, you can use the digital multi meter to check the dc power.
If the inverter does not produce the right amount of power, there may be several problems — all of which you can easily check with the digital multi meter like Blown fuse, Tripped breaker, Broken wires.
Use the digital multi meter to measure the output ac side of the inverter; the load on the inverter might have a current demand that’s too high. With the dual display showing ac voltage and frequency, you can determine whether the inverter ac output is operating correctly.
The inverter may be tied into the local utility. The ac current output from the inverter fluctuates with the level of solar input on the array. The inverter maintains the correct output voltage and phase to the utility. Any voltage problems from the utility may cause the inverter to shut down. In that event, contact the utility for repairs.
Troubleshooting Combiner Boxes
When you’re troubleshooting combiner boxes, amperage measurements and calculations are crucial to establishing whether the PV arrays are operating correctly. Measuring current on individual arrays or combining current measurements will help you determine if a cell has malfunctioned.
The thinner jaw design of the clamp meter lets you get several conductors in the jaw for combined current measurements, even in tight or crowded spaces like inverter or combiner boxes.


I really appreciate this post. I?¦ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again
Pingback: Solar PV plant Monitor and performance issues - Electricalsphere
Of course, what a magnificent website and revealing posts, I surely will bookmark your website.Have an awsome day!
Hiya, I am really glad I’ve found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossips and web and this is really irritating. A good blog with exciting content, that is what I need. Thanks for keeping this web-site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
Thanks a lot!
Please share my website to your friends group.
For more updates please Follow my Telegram/Whatsapp/Insta group
i do not make any newsletters.
Great insights
great article
Great post. I used to be checking constantly this
weblog and I’m impressed! Very useful information specifically the final part 🙂 I deal with such information a lot.
I used to be looking for this certain info for a long
time. Thank you and best of luck.
Pingback: Solar Energy generation impact on Power Grid
Pingback: Off Grid Solar Systems: Key Difference, Advantage and Disadvantage