What is Bundled Conductor?
For voltages in excess of 230 kV, it is in fact not possible to use a round single conductor. Instead of going in for a hollow conductor it is preferable to use more than one conductor per phase which is known as bundling of conductors. A bundle conductor is a conductor made up of two or more sub-conductors and is used as one phase conductor. It is found that the increase in transmission capacity justifies economically the use of two conductor bundles on 220 kV lines.
The following are the advantages in using bundle conductors:
- Reduced reactance.
- Reduced voltage gradient.
- Reduced corona loss.
- Reduced radio interference.
- Reduced surge impedance.
The reactance of the bundle conductors is reduced because the self GMD of the conductors is increased and as we know reactance = K ln GMD/GMR and as GMR is increased the reactance is reduced.
Theoretically, there is an optimum sub-conductor spacing for bundle conductors that will give minimum gradient on the surface of a sub-conductor and hence highest disruptive voltage. For a two conductor bundle, the equation for maximum gradient at the surface of a sub-conductor is
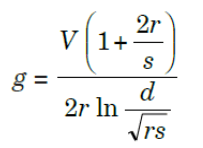
where s is the separation between the sub-conductors. Because of the effect of the sub-conductor son each other, the gradient at the surface of a sub-conductor is not uniform. (It varies co sinusoidal manner from a maximum at a point on the outside surface on the line of centres, to a minimum at the corresponding point on the inside surface.) The optimum spacing between sub-conductors for reducing voltage gradient is eight to ten times the diameter of the conductor regardless of the number of sub-conductors per phase.
Since the voltage gradient is reduced by using bundled conductors the radio interference is also reduced.
Finally we know that surge impedance of a line is given by L / C , where L is the inductance and C is the capacitance per unit length of the line. Since by bundling, the self GMD is increased, the inductance is reduced and capacitance increased, as a result the surge impedance is reduced. This in turn means that the maximum power that can be transmitted is increased. Therefore, for large power transmission at higher voltages bundled conductors should be used.
The procedure for calculating the reactance of the bundled conductor is same as for composite conductors. The basic difference between a composite conductor and bundled conductor is that the sub-conductors of a bundled conductor are separated from each other by a distance of almost 30 cms or more and the wires of a composite conductor touch each other.


Pingback: Conductor damaged due to use of PG Clamp