Table of Contents
ToggleEnergy meter or Watt hour meter
Single phase induction type energy meter is also popularly known as watt-hour meter. This name is given to it. Induction type energy meter essentially consists of following components:
1.Driving system
- Moving system
- Braking system
- Registering system
Construction and Layout of Energy meter or Watt hour meter
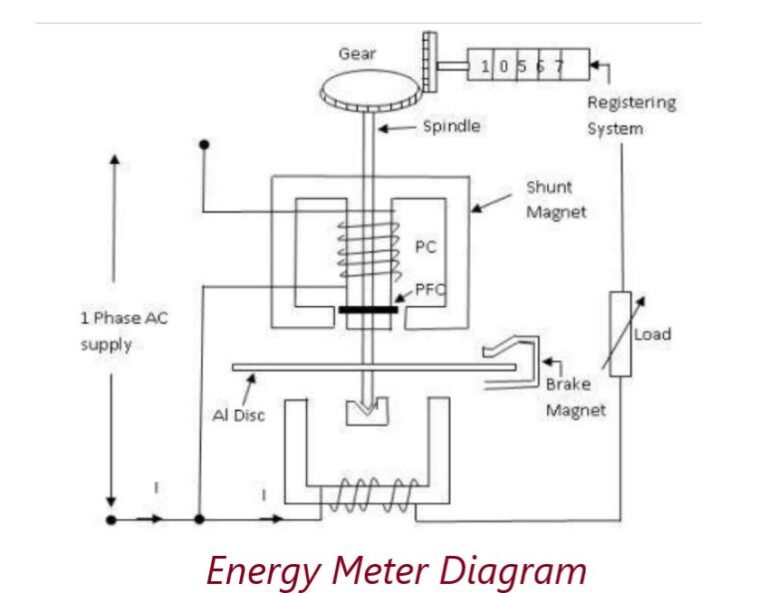
Driving system
The driving system of the meter consists of two electro-magnets.The core of these electromagnets is made up of silicon steel laminations. The coil of one of the electromagnets is excited by the load current. This coil is called the current coil.
The coil of second electromagnet is connected across the supply and, therefore, carries a current proportional to the supply voltage. This coil is called the pressure coil. Consequently the two electromagnets are known as series and shunt magnets respectively.
Copper shading bands are provided on the central limb. The position of these bands is adjustable. The function of these bands is to bring the flux produced by the shunt magnet exactly in quadrature with the applied voltage.
Moving system
This consists of an aluminium disc mounted on a light alloy shaft. This disc is positioned in the air gap between series and shunt magnets. The upper bearing of the rotor (moving system) is a steel pin located in a hole in the bearing cap fixed to the top of the shaft.
The rotor runs on a hardened steel pivot, screwed to the foot of the shaft. The pivot is supported by a jewel bearing. A pinion engages the shaft with the counting or registering mechanism.
Braking system
A permanent magnet positioned near the edge of the aluminium disc forms the braking system. The aluminium disc moves in the field of this magnet and thus provides a braking torque.
The position of the permanent magnet is adjustable, and therefore braking torque can be adjusted by shifting the permanent magnet to different radial positions.
Registering system
The function of a registering or counting mechanism is to record continuously a number which is proportional to the revolutions made by the moving system.
By a suitable system, a train of reduction gears the pinion on the rotor shaft drives a series of five or six pointers. These rotate on round dials which are marked with ten equal divisions.
Working principle of Energy meter
The working of single phase induction type energy meters are based on two main fundamentals:
- Rotation of aluminium disk.
- Arrangement of counting and displaying the amount of energy consumed
Rotation of an Aluminium Disk
The rotation of metallic disk is operated by two coils. Both the coils are arranged in such way that one coil produces a magnetic field in proportion to voltage and the other coil creates a magnetic field proportion to current.
The field produced by voltage coil is delayed by 900 so that eddy current is induced in the disk. The force exerted on the disk by the two fields is proportional to the product of the immediate current and voltage in the coils.
As a result of it, a lite weight aluminium disk rotates in an air gap. But there is a need to stop a disk when there is no power supply. A permanent magnet works as a brake which opposes the rotation of the disk and balances the speed of rotation with respect to power consumption.
Arrangement of Counting and Displaying the Energy Consumed
In this system, the rotation of the floating disk has been counted and then displayed on the meter window. The aluminium disk is connected to a spindle which has a gear.
This gear drives the register and the revolution of the disk has been counted and displayed on the register which has series of dials and each dial represent a single digit.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
What is an energy meter?
An energy meter, also known as an electricity meter or watt-hour meter, is a device used to measure and record the amount of electrical energy consumed by a residential, commercial, or industrial customer.
How does an energy meter work?
Energy meters work by measuring the amount of electrical energy passing through them. They typically use a spinning disc, digital display, or electronic circuitry to measure the voltage and current flowing through a circuit and calculate the energy consumption over a given period.
What are the different types of energy meters?
There are several types of energy meters, including electromechanical meters, electronic meters, smart meters, and prepaid meters. Each type has its own method of measuring and recording energy consumption, as well as features for data communication and remote monitoring.
What is the importance of an energy meter?
Energy meters play a crucial role in billing customers for their electricity consumption, as well as in monitoring and managing energy usage. They help utilities accurately measure and track energy consumption, detect theft or tampering, and promote energy conservation.
How accurate are energy meters?
Energy meters are designed to be highly accurate within specified tolerances. They undergo rigorous testing and calibration to ensure accuracy in measuring energy consumption over a wide range of operating conditions.
How often should energy meters be tested for accuracy?
Energy meters are typically tested for accuracy during manufacturing and periodically throughout their service life. The frequency of testing depends on factors such as regulatory requirements, meter type, and usage patterns.
What are the benefits of smart meters compared to traditional meters?
Smart meters offer several advantages over traditional meters, including:
- Remote reading and monitoring of energy consumption.
- Real-time data on energy usage, allowing customers to track and manage their usage more effectively.
- Improved accuracy and billing transparency.
- Support for time-of-use pricing and demand response programs.
- Enhanced capabilities for utilities to detect and respond to outages and power quality issues.
How do prepaid energy meters work?
Prepaid energy meters allow customers to pay for electricity in advance


yoou are actually a good webmaster. The website loading
pace is amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick.In addition, The contents are masterpiece.
you have donee a great process in this topic! https://www.Waste-ndc.pro/community/profile/tressa79906983/
you aree actually a good webmaster. The website loading pace
is amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. In addition, The cpntents are masterpiece.
you have donbe a great process in this topic! https://www.Waste-ndc.pro/community/profile/tressa79906983/
Pingback: Direct Loading Test on Single Phase Transformer and Three Phase Induction Motor - Electricalsphere