Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Flexible Alternating Current Transmission or FACTs
FACTS as they are generally known, are new devices that improve transmission systems and it is a static equipment used for the AC transmission of electrical energy.It is generally a power electronics based device. Meant to enhance controll ability and increase power transfer capability.
FACTS is an acronym for Flexible AC Transmission System and it is an application of power electronic devices to electrical transmission system. It is an AC transmission system that incorporates a power electronic controller and other static controllers to improve the controllability as well as power transfer capability. It improves the performance of electrical networks by managing active and reactive power.
Introduction
The electric power supply systems of whole world are interconnected, involving connections inside the utilities, own territories with external to inter-utility, internationals to inter regional and then international connections.
This is done for economic reasons, to reduce the cost of electricity and to improve reliability of power supply. We need the interconnections to pool power plants and load centres in order to minimize the total power generation capacity and fuel cost. Transmission lines interconnections enable to supply, electricity to the loads at minimized cost with a required reliability.
The FACTS Technology is adopted in the transmissions to enhance grid reliability and to over come the practical difficulties which occur in mechanical devises used as controllers of the transmission network.
The electric power supply systems of whole world are interconnected, involving connections inside the utilities, own territories with external to inter-utility, internationals to inter regional and then international connections. This is done for economic reasons, to reduce the cost of electricity and to improve reliability of power supply.
We need the interconnections to pool power plants and load centres in order to minimize the total power generation capacity and fuel cost. Transmission lines interconnections enable to supply, electricity to the loads at minimized cost with a required reliability.
The FACTS Technology is adopted in the transmissions to enhance grid reliability and to over come the practical difficulties which occur in mechanical devises used as controllers of the transmission network.
Why Compensation Techniques are used in Power system?
Power System network consist of three kinds of powers, namely, active, reactive and apparent power. Active power is the useful or true power that performs a useful work in the system or load. Reactive power is caused entirely by energy storage components and the losses due to reactive power may be considerable, although reactive power is not consumed by the loads.
The presence of reactive power reduces the capability of delivering the active power by the transmission lines. And the apparent power is the combination of active and reactive power. In order to achieve maximum active power transmission, the reactive power must be compensated.
This compensation is necessary for
Improving the voltage regulation
Increasing system stability
Reducing the losses associated with the system
Improving the power factor
Better utilization of machines connected to the system
The compensation techniques of the power system supplies the inductive or capacitive reactive power (to its particular limits) in order to improve the quality and efficiency of the power transmission system. The following are the two popular compensation techniques used in power system.
Types of FACTs controlled device
FACTS controllers are classified as:
Series Controllers
Shunt Controllers
Combined Series-Series Controllers
Combined Series-Shunt Controllers
Series Controllers
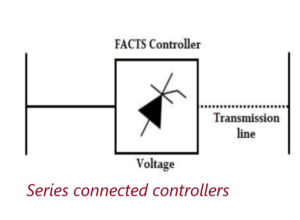
It could be a variable impedance (capacitor, reactor, etc) or a power electronic based variable source of main frequency, subsynchonous and harmonic frequencies to serve the desired need.
Series controller Inject a voltage in series with the line.If the voltage is in phase quadrature with the current, controller supplies or consumes reactive power.Any other phase, involves control of both active and reactive power.
These controllers could be variable impedance such as a reactor or capacitor or a power electronic based variable source. Examples of the series controllers include SSSC, TCSR, IPFC, TSSC, TCSC, and TCSR.
Shunt Controllers
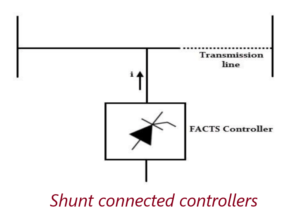
It could be a variable impedance (capacitor, reactor, etc) or a power electronic based variable source or combination of both.
Shunt ControllersInject a current in the system.If the current is in phase quadrature with the voltage, controller supplies or consumes reactive power.Any other phase, involves control of both active and reactive power.
Similar to the series connected controllers, these controllers could be a variable reactor or capacitor or a power electronic based variable source. Examples of the shunt controllers include TCR, STATCOM, TSR, TCBR and TSC.
Combined Series-Series Controllers
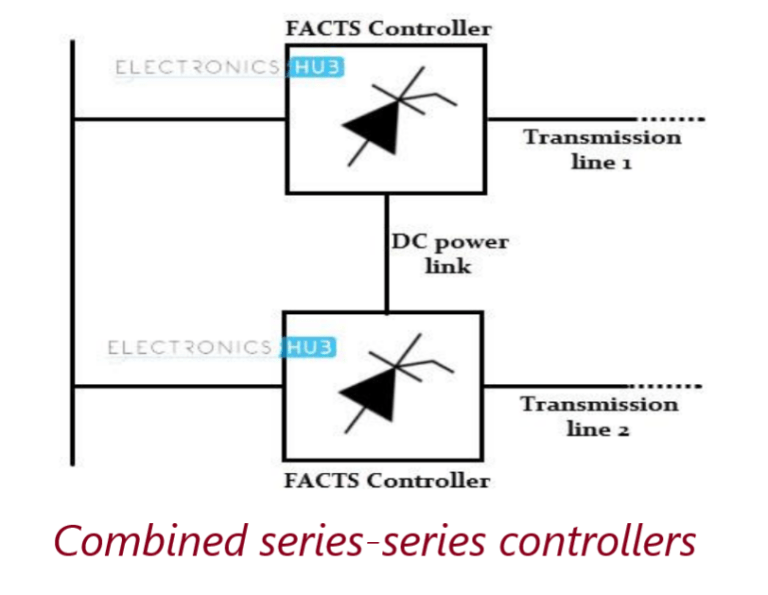
It could be a combination of separate series controllers or unified controller.Series controllers supply reactive power for each line and real power among lines via power link.Interline power flow controller balance real and reactive power flow in the lines.
Combined Series-Shunt Controllers
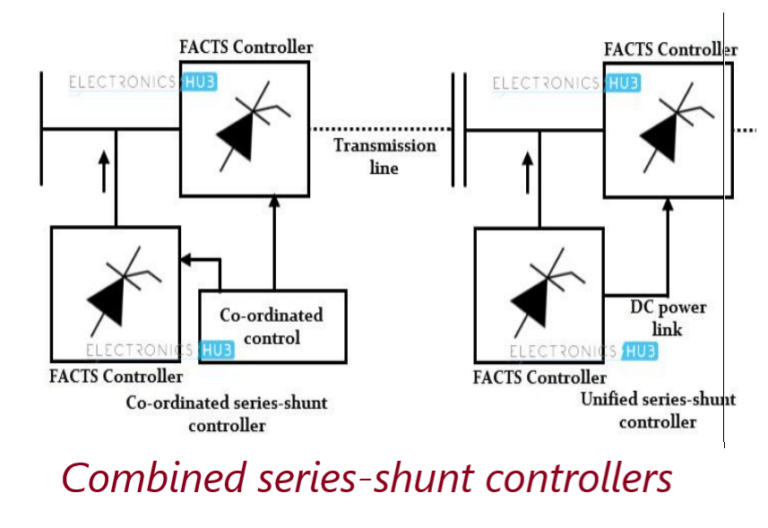
It could be a combination of separate series & shunt controllers or unified power flow controller.
Combined Series-Shunt ControllersInject current into the system with the shunt controller and voltage in series with the line with series controller.When the controllers are unified, exchange real power between series and shunt controllers via power link.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
What are FACTs devices?
FACTs devices are power electronic-based systems used to enhance the controllability and flexibility of AC transmission systems. They are designed to improve the efficiency, stability, and reliability of power systems.
What is the purpose of FACTs devices?
FACTs devices are deployed to address various challenges in power systems, such as voltage control, power flow control, stability enhancement, and grid reliability improvement.
How do FACTs devices work?
FACTs devices utilize power electronics technology to control voltage, impedance, and phase angle of AC transmission lines. By adjusting these parameters, FACTs devices can regulate power flow, stabilize the grid, and mitigate voltage fluctuations.
What are some common types of FACTs devices?
Common FACTs devices include Static Var Compensators (SVCs), Static Synchronous Compensators (STATCOMs), Thyristor-Controlled Series Capacitors (TCSCs), Thyristor-Controlled Phase Shifters (TCPSs), and Unified Power Flow Controllers (UPFCs).
What are the challenges associated with deploying FACTs devices?
Challenges include high initial costs, complex engineering and integration requirements, potential electromagnetic interference, and regulatory hurdles. Additionally, ensuring interoperability with existing grid infrastructure can be a challenge.
Are there any environmental benefits associated with FACTs devices?
Yes, FACTs devices can contribute to the efficient utilization of renewable energy resources by facilitating their integration into the grid. By improving grid stability and reducing transmission losses, FACTs devices indirectly support the adoption of clean energy technologies.
How do FACTs devices contribute to grid modernization efforts?
FACTs devices play a crucial role in modernizing power grids by enabling greater control, flexibility, and resilience. They facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, support the electrification of transportation, and enhance grid reliability in the face of evolving demand patterns and cybersecurity threats.
What is the future outlook for FACTs technology?
A: The future of FACTs technology is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on enhancing device performance, reducing costs, and expanding functionality. As power systems continue to evolve, FACTs devices will play an increasingly vital role in ensuring the reliability and sustainability of the grid.
What benefits do FACTs devices provide to power systems?
FACTs devices offer several benefits, including increased transmission capacity, improved voltage stability, enhanced transient stability, reduced line losses, and better utilization of existing infrastructure.
Where are FACTs devices typically installed in power systems?
FACTs devices are installed at strategic locations within the power grid, such as substations or along transmission lines, to address specific operational requirements and optimize system performance.
