Table of Contents
ToggleWhy single-phase induction motors are not self-started?
Single phase induction motor has single phase distributed winding in stator and a squirrel-cage rotor.
When Single phase supply is applied to single phase stator winding an alternating flux (field) is produced in stator.
Alternating flux varied with space (single) axis only and it’s not a constant magnitude synchronously revolving (rotating) flux as in the case of a two or a three phase stator winding fed from a 2 or 3 phase supply.
Now, an alternating or pulsating flux acting on a stationary squirrel-cage rotor cannot produce rotation due to rotor inertia (only a revolving flux can produce rotation).
That is why a single phase motor is not self-starting.
Why synchronous motors are not self-started?
Synchronous motor start rotating only if Magnetic locking is ensuring between stator poles & rotor poles (Ns –Sr & Ss- Nr).
Magnetic locking is not possible as stator poles are rotating at very high synchronous speed (3000 rpm, for 50 Hz & 2 pole) and rotor pole has zero speed and high inertia at starting.
Due to that motor fail to start which can be explain by following figures.
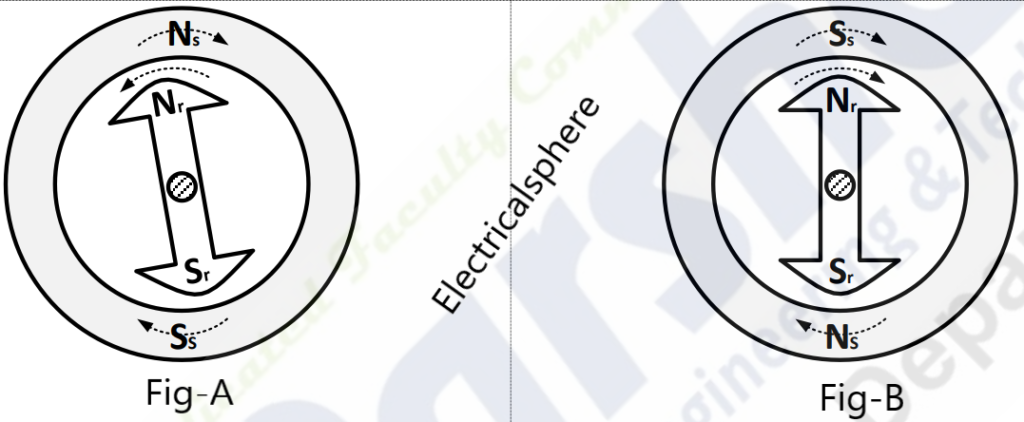
Fig. A show one particular instant of stator and rotor pole. At this particular instant rotor and stator poles might be of the same polarity (Ns-Nr or Ss-Sr) causing a repulsive force on the rotor. Due to this repulsive force rotor try to rotate in anticlockwise direction.
After a fraction of seconds (10 ms), the stator polarities will change to that as shown in Fig. B. Here the instantaneous torque produced on the rotor is in clockwise direction due to the attraction of unlike poles (Ns-Sr or Ss-Nr).
As it tries to rotate in clockwise direction but again stator pole change (Fig. A) and repulsion torque will produced again.
Due to the inertia of the rotor, it cannot respond to such quickly reversing torques. So the motor is subjected with a pulsating torque. Hence synchronous motor is not self-starting.
Methods of Starting the Synchronous Motor
To make SM self-starting, some techniques will use which initially rotates the rotor very close to synchronous speed in the direction of the magnetic field.
On achieving this speed, rotor pulled into synchronism with stator pole and due to that magnetic locking occurs.
After magnetic locking, the synchronous motor continues to rotate even after removal of external mechanism. Different Starting methods used in synchronous motor, like
1.Starting as Induction motor with damper winding and slip ring
- Starting with Low Supply Frequency
3.Starting with Prime Mover with DC motor or excitor and small induction motor.
Making Single phase induction motor self-starting
If we make the stator flux rotating type, rather than alternating type, which rotates in one particular direction only, then the induction motor will become self-starting.
For producing this rotating magnetic field, we require two alternating flux, having some phase difference angle between them. When these two fluxes interact with each other, they will produce a resultant rotating flux.
This resultant flux is rotating in nature and rotates in space in one particular direction only.
This rotating magnetic field is cut by rotor conductors, emf is produced, rotor current flows and finally force is exerted on current carrying rotor conductors by rotating magnetic field.
Thus torque is produced on rotor to rotate it.
To produce two alternating fluxes with some phase difference angle between them, single-phase winding is split up into two parts, called Split-phase winding.
These two parts (windings) are placed 90° apart in space and two currents 90°displaced in time-phase are passed through them.
The phase displacement between two-winding (phase) currents can be achieved by adjusting parameters (R & L) of split-phase windings or connecting capacitor in series with one of the phase windings.
The rotating magnetic field can also be produced by using shaded-pole construction, wherein the pole is divided into two sections: shaded portion and non-shaded portion. The portion of core round which a shading band of copper is placed is called shaded portion. Only one winding is used. When winding is excited from AC supply, the shaded pole construction produces rotating magnetic field effect i.e shifting of magnetic field from non-shaded potion to shaded portion.
Thus any arrangement that produces rotating magnetic field using single-phase AC supply can be used to self-start the motor.
Application of Single-Phase Induction Motors
The most common applications are table fans, exhaust fans, hair driers, fans for refrigeration and air-conditioning equipment’s, electronic equipment, cooling fans etc.
They are also used in record players, tape recorders, slide projectors, photocopying machines, in starting electric clocks and other single-phase synchronous timing motors.

Pingback: Faults in induction motor and Thermal overload protection of Induction Motor
Pingback: Start and Stall protection of Induction Motor
Pingback: Capacitor Start and Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Induction Motor - Electricalsphere
Greate pieces. Keep posting such kind of info on your site.
Im really impressed byy your blog.
Hello there, You’ve done an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and individually recommend
to my friends. I’m confident they will be benefited from this web site. https://zeleniymis.com.ua
Greate pieces. Keeep poeting such kind of info on your site.
Im really impresed by your blog.
Hello there, You’ve dohe an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg
it and indiviidually recommewnd too my friends.
I’m confident thy will be benefited from this web site. https://zeleniymis.com.ua
Pingback: Types of single phase induction motors and their diagram - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Objective (MCQ) question on Induction Motor
Pingback: Objective (MCQ) on Synchronous Motor
Balanceo dinamico
Aparatos de equilibrado: clave para el operación uniforme y productivo de las máquinas.
En el campo de la avances contemporánea, donde la rendimiento y la seguridad del sistema son de gran trascendencia, los sistemas de calibración cumplen un función fundamental. Estos dispositivos específicos están diseñados para balancear y estabilizar elementos rotativas, ya sea en herramientas industrial, medios de transporte de desplazamiento o incluso en equipos de uso diario.
Para los profesionales en reparación de equipos y los técnicos, trabajar con dispositivos de equilibrado es crucial para asegurar el rendimiento suave y fiable de cualquier sistema giratorio. Gracias a estas alternativas avanzadas modernas, es posible disminuir considerablemente las movimientos, el ruido y la carga sobre los soportes, prolongando la tiempo de servicio de piezas importantes.
Igualmente relevante es el función que desempeñan los equipos de balanceo en la atención al consumidor. El apoyo especializado y el reparación continuo aplicando estos dispositivos permiten dar servicios de alta nivel, incrementando la bienestar de los consumidores.
Para los responsables de negocios, la aporte en unidades de equilibrado y detectores puede ser esencial para aumentar la efectividad y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es principalmente trascendental para los dueños de negocios que administran medianas y pequeñas empresas, donde cada punto importa.
Asimismo, los aparatos de calibración tienen una amplia aplicación en el ámbito de la protección y el monitoreo de excelencia. Posibilitan localizar potenciales defectos, impidiendo mantenimientos onerosas y perjuicios a los equipos. Más aún, los información recopilados de estos dispositivos pueden usarse para maximizar procesos y potenciar la visibilidad en sistemas de consulta.
Las sectores de aplicación de los aparatos de calibración incluyen numerosas ramas, desde la producción de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el supervisión del medio ambiente. No afecta si se habla de enormes manufacturas productivas o modestos locales domésticos, los dispositivos de balanceo son indispensables para asegurar un funcionamiento óptimo y sin presencia de fallos.