Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Cross linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated single core and multicore cables are manufactured with colours of cores red, yellow, blue to represent phase R, Y, B respectively and black colour to represent neutral N.
Construction of XLPE insulated cables are similar to that of PVC cables. Therefore they have all the advantages of PVC cables in terms of cleanliness., ease of handling and simple jointing and terminations.
The basic physical difference is that XLPE cables are more robust thus allowing the thickness to be reduced which in turn allows a corresponding reduction in the over all size of the cables.
These cables are suitable for use where combination of ambient temperature and temperature rise due to load results in conductor temperature not exceeding 90°C under normal operation and 250° C under short circuit condition.
Construction of XLPE cable
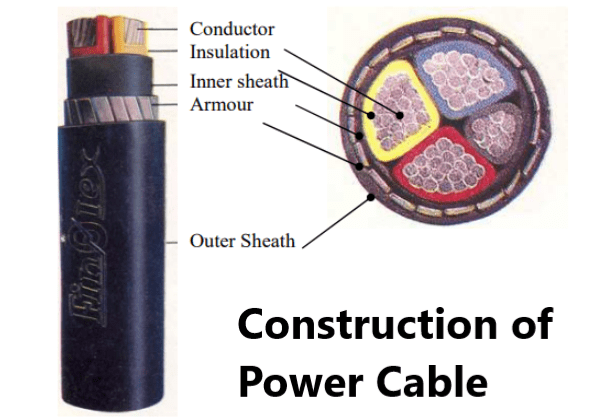
Conductor : The conductor is made of electrical grade aluminium or copper. Generally all power cables have aluminium as the conductor. The conductor shall be of stranded construction size 2.5 sq mm. and above.
Conductor Screening : Cables rated for 6.35/11 kV are provided with conductor screening over the conductor by applying non-metallic semi-conducting tape or by extrusion of semi-conducting compound or a combination of the both.
Insulation : PVC compound is applied to the conductors by the extrusion process. It is so applied that it can be removed without damaging the conductor.
Insulation screening : Cables rated for 6.35/11 kV are provided with insulation screening. It consists of two parts, namely non-metallic (semi-conducting) and metallic.
Inner sheath (for multi core cables):The laid up cores are surrounded by an inner sheath of any of the following types. a. Extruded PVC compound (for armoured cables) b. Wrapping of PVC/plastic tapes. (for unarmoured cables). Inner sheath is also known as bedding in case of armoured cables.
Armouring: Depending upon the application these cables can be armoured or unarmoured. For single core cables flat aluminium wire armour is used, since aluminium being a non magnetic material, will not induce stray current. For multi core cables, galvanized round or flat steel wire armour or double steel tape armour is used. The armouring is applied over the core insulation or inner sheath in case of single core cables and over the inner sheath in case of multicore cables.
Outer sheath: Outer sheaths are made of black polyvinyl chloride (PVC) compound, which protect the armour material from corrosion. This PVC compound is applied by extrusion method. Outer sheath is applied over the nonmagnetic metallic tape covering the insulation or over the non-magnetic metallic part of insulation screening in case of unarmoured single core cables and over the armouring in case of armoured cables.
Low Voltage XLPE Cables
These cables are suitable for use on ac single phase or three phase (earthed or unearthed) systems for rated voltages up to and including 1100 V. These cables may be used on dc systems also for rated voltage up to and including 1500V to earth. These cables are generally available in following configurations.
Low Voltage XLPE Insulated, Unarmoured, PVC Sheathed Cables.
These cables are designed for general purpose indoor power distribution application. Plain circular or sector shaped stranded annealed aluminium or copper conductors are used and insulation of core consists cross linked polyethylene. For multicore cables, cores are laid up together and filled with non-hygroscopic material (plastic fillers) compatible with the insulation. Outer sheath consists of black colour PVC type ST2.
Low voltage XLPE Insulated, Screened, PVC Sheathed Cables
Design of the these cables are same as Low Voltage XLPE Insulated, Unarmoured, PVC Sheathed Cablesexcept that aluminium mylar tape or annealed copper wire or tinned copper braid is used as screen material over XLPE insulation. Screening prevents external electro magnetic influences to the cable.
Low voltage XLPE insulated armoured PVC sheathed cables
Constructional features of single core aluminium armoured cables and multicore steel wire armoured cables are similar to PVC insulated cables. These cables are most suitable for under ground power distribution application, where there is a risk of mechanical damages.
Medium Voltage XLPE Cables
Cross linked polyethylene insulated and PVC sheathed medium voltage power cables are suitable for voltages from 3.3 kV and up to and including 33kV. Following categories of armoured screened or unscreened single core and three core XLPE insulated and PVC sheathed cables are available for electricity supply purposes.
- Earthed system (Uo/U) – 1.9/3.3kV, 3.8/6.6kV, 6.35/11kV, 12.7/22kV and 19/33kV.
- Unearthed system – 3.3/3.3kV, 6.6/6.6kV and 11/11kV.
In these cables conductors are compacted stranded aluminium of smooth profile, free from sharp juts that could damage the insulation due to high local electric stresses.
XLPE insulation is processed using the triple layer dry curing extrusion method. These cables are supplied with extruded cross linked semi conducting screens to protect the main solid XLPE insulation. The conductor screen fills the interstices between wires and provides a smooth circular envelope around the conductor. This diminishes the concentration of flux lines around the individual wires and hence the electrical stress around the conductor.
Semi conductive insulation screen either strippable or bonded is applied over the core insulation. A layer of annealed un coated copper tapes or copper wires is provided over the extruded insulation screen. This metallic screen provides an earthed envelope. This metallic shield provides protection from external fields, reduced stress concentration and uniform radical field lines from conductor and does not cause induced current.
66kV High voltage XLPE Cable
66 kV HV power cable is a high-voltage cable used for electric power transmission at a voltage rating of 66 kilovolts or 66000 volts. These cables are designed to handle high voltages and are typically used in medium to high-voltage power transmission systems. These cables are often used in power systems to move electrical power from one place to another.
66 kV HV power cables are commonly made with a central conductor built from copper/aluminium. This conductor is covered in a layer of insulation materials like XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene). An outer covering is typically made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PE (polyethylene) which provides an additional layer of protection. The insulation materials are particularly engineered to meet the intense voltage and electrical strain experienced during the power transmission.
66 KV HV power cables have several features that make them suitable for high-voltage power transmission. Some of these features are:
High-voltage capability: The cables can handle up to 66 KV or 66,000 volts and this feature makes them ideal for use in applications such as utilities, industrial plants, and other areas that require high-voltage power.
High performance & Cost effective: 66 KV HV Power Cables deliver exceptional performance and provide long service life with minimal maintenance costs.
High current-carrying capacity: Current-carrying capacity of this cable is high, which enables it to transmit large amounts of power over long distances while minimizing losses.
Superior insulation properties: The cables are insulated with cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), which is designed specifically to withstand the high voltage and electrical stress encountered during power transmission.
Strong Construction: 66 KV HV power cables usually have a central conductor made of copper or aluminium. This conductor is surrounded by layers of insulation materials like XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene). Finally, there’s an outer sheath made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PE (polyethylene).
Advantage of XLPE power cable over PVC cable
Excellent electrical & physical properties: High resistance to thermal deformation and the ageing property of XLPE cables provides greater continuous and short circuit current capacity ensuring higher degree of reliability over wide range of temperature variation as compared to PVC cables.
Higher current carrying capacity: Current carrying capacity of XLPE cables of the same size is approximately 20 to 30% higher than that of PVC due to higher operating temperature.
Resistant to heat: With cross-linked molecules structure, XLPE cables are excellently ozone resistant and provide outstanding stability and are resistant to heat.
XLPE cables have lower dielectric loss, lower permitivity as compared to PVC cables.
Due to lower specific gravity, XLPE cables are comparatively lighter in weight than PVC cables, therefore, ease in handling, laying and installation. The cable requires less supporting due to low weight.
XLPE cable has higher mechanical properties and more robust as compared to PVC cables due to thermosetting process.


Hikaye paylaşımı Google SEO ile web sitemizin trafiği gözle görülür şekilde arttı. http://www.royalelektrik.com/esenyurt-elektrikci/
Pingback: What Is Cable Insulation? - EBM MACHINE
Terrific data. Many thanks!
online casino jurisdictions https://combatcasino.info/live-online-casinos/ city of dreams online casino
Pingback: How to locate Cable fault - Electricalsphere
I am so happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the accidental misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.
Hey very cool site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds I’m satisfied to find a lot of helpful information here in the submit, we need develop extra strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
Thanks a Lot!
share my post to your friends to appreciate my work.
Keep learning.
Perfect piece of work you have done, this website is really cool with fantastic information.