Table of Contents
ToggleCapacitor Start Induction Motor
The construction of this type of motors is similar to the resistance split phase type. The difference is that in series with the auxiliary winding the capacitor is connected. The capacitive circuit draws a leading current, this feature used in this type to increase the split phase angle α between the two currents Im and Ist . Depending upon whether capacitor remains in the circuit permanently or is disconnected from the circuit using centrifugal switch, these induction motors are classified as,
- Capacitor Start motor
- Capacitor Start Capacitor Run motor
Capacitor Start Motor
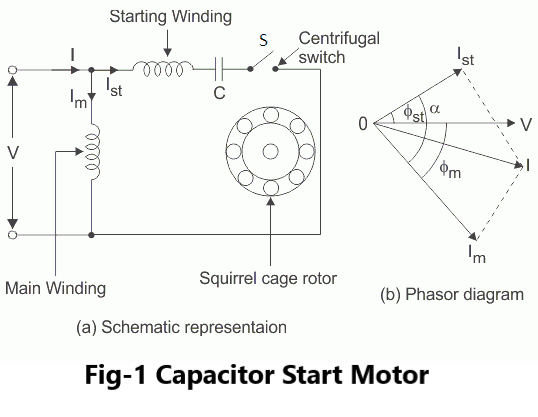
A Capacitor Start Motor are a single-phase Induction Motor that employs a capacitor in the auxiliary winding circuit to produce a greater phase difference between current in the main and the auxiliary windings. The name capacitor itself shows that the motor uses a capacitor for the purpose of starting. The figure below shows the connection diagram of a Capacitor Start Motor.
The Capacitor start motor has a Cage rotor and has two windings on the stator. They are known as the main winding and the auxiliary or the starting winding. The two windings are placed 90 degrees apart. A capacitor Cs is connected in series with the starting winding. A centrifugal switch Sc is also connected in the circuit.
When the stator windings are energized from a1-phase supply, the main winding carries current Im and the starting winding carries current Ia. The current Im lags the voltage by angle Φm while due to capacitor the current Ist leads the voltage by angle Φst. Hence there exists a large phase difference (‘α ‘) between the two currents which is almost 90 degree which is an ideal case. The starting torque is proportional to ‘α ‘and hence such motors produce very high starting torque The phasor diagram is shown in the Fig.1(b).
The main and auxiliary windings are connected in parallel during motor starting. When motor speed approaches to 75 to 80% of the synchronous speed, the starting winding gets disconnected due to operation of the centrifugal switch. The capacitor remains in the circuit only at start hence it is called capacitor start motors.
Capacitor Start Capacitor Run motor
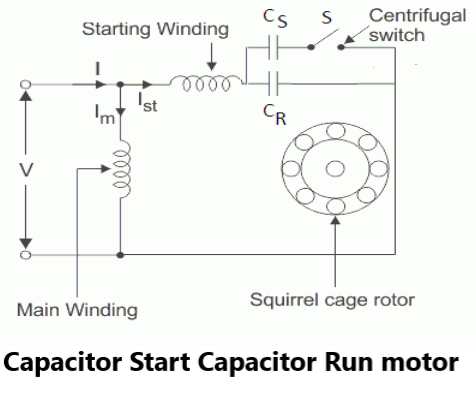
The Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor has a cage rotor and its stator has two windings known as Main and Auxiliary Windings. The two windings, one of which is directly connected to the source. The other winding is also connected to the source, but in series with a capacitor (starting capacitor).
The capacitor-fed winding has a large number of turns of relatively small wire, compared to the directly connected winding. There is no centrifugal switch it means that the capacitor is permanently connected in the circuit. As the capacitor is permanently connected it is also called as Permanent Spilt Capacitor Run Motor.
The phasor diagram remains same as shown in the Fig.1(b). The performance not only at start but in running condition also depends on the capacitor C hence its value is to be designed so as to compromise between best starting and best running condition. It has a high-power factor on account of the capacitor and no centrifugal switch is required. However, the starting torque is low.
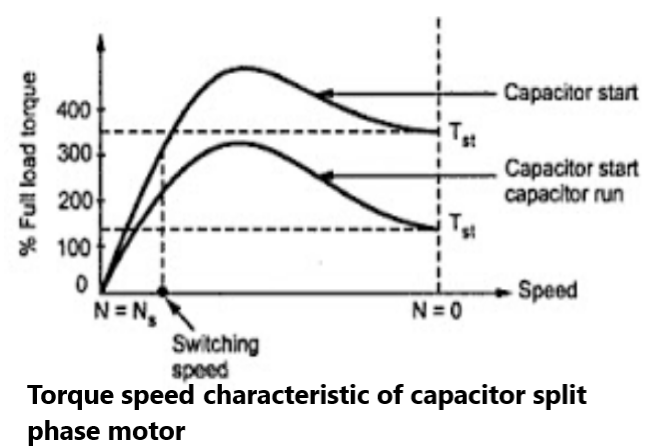
The direction of rotation, in both the types can be changed by interchanging the connection of main winding or auxiliary winding. The capacitor permanently in the circuit improves the power factor. These motors are more costly than split phase type motors. The capacitor value can be selected as per the requirement of starting torque, the starting torque can be as high as 350 to 400 % of full load torque.
In case of capacitor start capacitor run motor, there is no centrifugal switch and capacitor remain permanently in the circuit. This improves the power factor.
Application
The capacitor start motors have high starting torque and hence are used for hard starting loads. These are used for compressors, conveyors, grinders, fans, blowers, refrigerators, air conditions etc. These are most commonly used motors.
The capacitor start capacitor run motors are used in celling fans, blowers and air-circulations. These motors are available up to 6 kW.
Comparison between Capacitor Start and Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor
Capacitor Start Motor
The capacitance of the start capacitor is more than the run capacitor.
It provides the initial electric push to start the motor.
It has a very high starting torque.
The start capacitor increases the motor starting torque and draws the motor to be cycle on and off rapidly.
Start capacitor are rated in a range of 70 or more micro-Farad (µF).
The start capacitor creates a current to voltage lag in the separate start windings of the motor.
The start capacitor will provide initial push to the motor.
Capacitor Start Capacitor Run motor
The capacitance of Capacitor C depends on starting and running condition.
It provides power to the motor.
It has a low starting toque.
Since there is no centrifugal switch, the Starting torque is low.
Run capacitor are rated in a range of 3-70 micro-Farad (µF).
The run capacitor uses the charge in the dielectric to boost the current which provides power to the motor.
If the wrong run capacitor is installed the motor will not have an even Magnetic Field.

Pingback: Types of single phase induction motors and their diagram
Pingback: Interview Question on Electrical Motor
Pingback: Ceiling Fan: Construction , Working and Fault solution - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Table Fan: Construction and Working - Electricalsphere