Table of Contents
ToggleMCCB full name
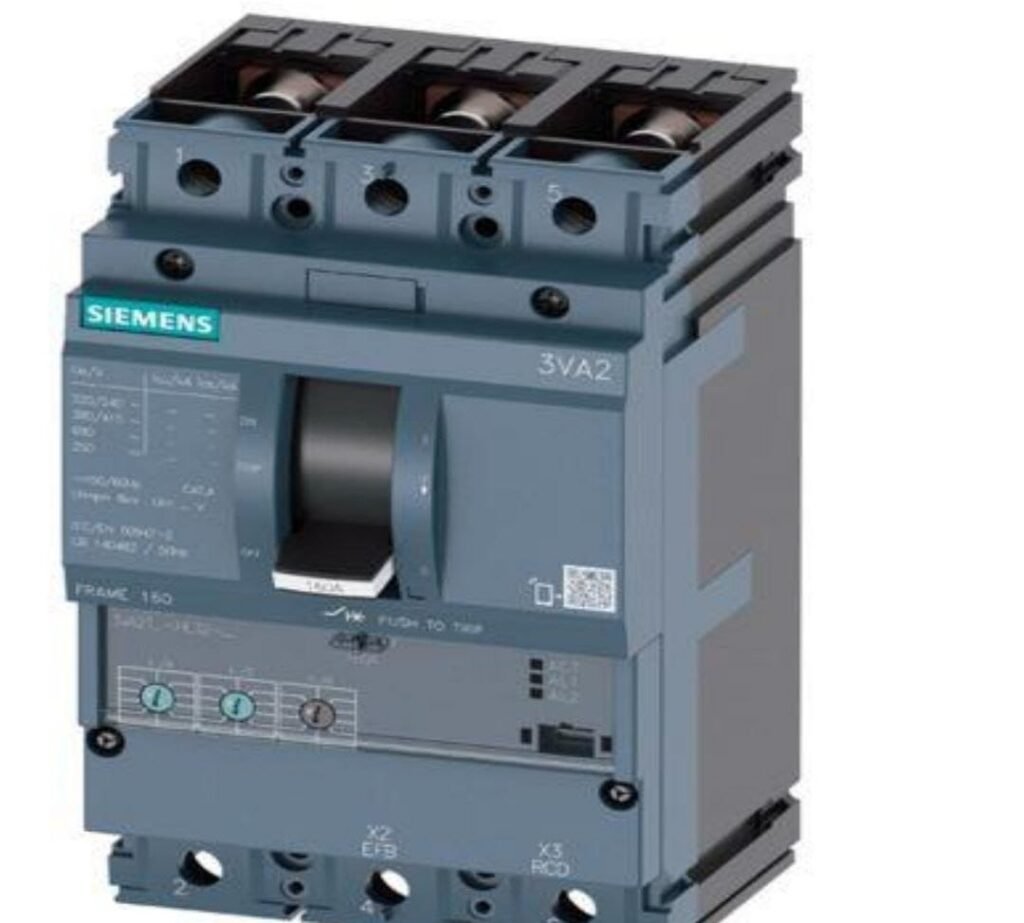
MCCB-Moulded Case Circuit Breakers
Difference between MCCB and MCB
MCCBs have higher fault current withstand capacities compared to MCBs.
MCBs – 4.5kA, 6kA, 10kA and 16kA (rarely).
MCCBs – 25kA, 36kA, 50kA, 65kA and 100kA.
So, MCCBs are required to be used in places where the fault current rating is high and MCB used for lower current application. MCCBs are available from 20A to 2500A and in different poles such as SP, DP, TP and 4P.

MCCBs Application
Overload protection.
Short circuit protection.
Isolation / Disconnection.
Overload protection is achieved by a bimetallic contact as in the case of MCBs. Short circuit protection is achieved based on the principle of electromagnetism.
Characteristics of MCCBs
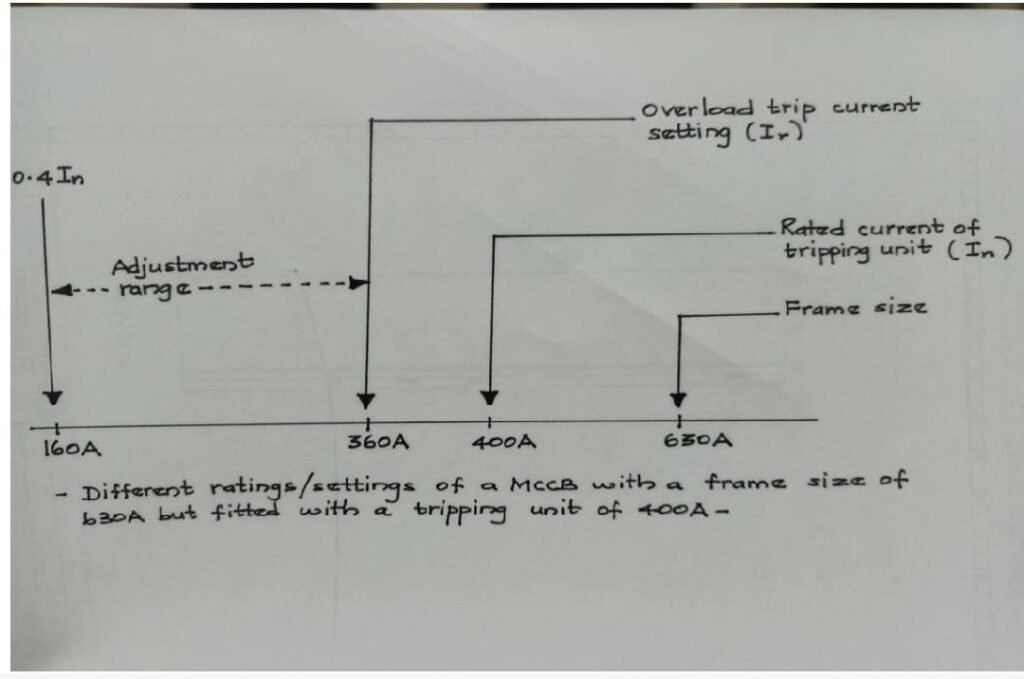
(a) Rated Frame Current (Inm)
This refers to the maximum current that the MCCB is rated to handle. This defines the upper limit of the adjustable trip unit.
(b) Rated Current (In)
This refers to the current that determines when the MCCB trips due to overload protection. This can be adjusted to a maximum of the Inm.
(c) Rated Insulation Voltage (Ui)
This refers to the maximum voltage which MCCB can resist in lab conditions.
(d) Rated Working Voltage (Ue)
This value is the rated voltage for the continuous operation of the MCCB. This is normally the same as or close to the system voltage.
(e) Rated Impulse Withstand Voltage (Uimp)
This determines the ability of the MCCB to withstand transient over voltages. The size of the impulse used for this testing is 1.2/50 µs.
(f) Service / Operating Short Circuit Breaking Capacity (Ics)
This is the maximum fault current that a MCCB can handle without being permanently damaged. MCCBs are generally reusable after fault interruption operation provided that they do not exceed Ics. The higher the Ics, the more reliable the MCCB is. This is the maximum fault current value that a MCCB can handle.
(g) Ultimate Short Circuit Breaking Capacity (Icu)
If the fault current exceeds this value, the MCCB will be unable to trip. In other words, if the fault current exceeds Ics but does not exceed Icu, the MCCB can still remove the fault, but may be damaged and require replacement.
(h) Overload Relay Trip Current (Ir)
There are two types of trip units for the MCCBs; Electronic Trip Unit (E) and Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit (TM).
The trip unit in the E type MCCBs can be adjustable in the range of 0.4 – 1.0 times In (0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9 and 1.0).
The trip unit in the TM type MCCBs can be adjustable in the range of 0.8 – 1.0 times In (0.8, 0.9 and 1.0).
In = 400A
Ir = 400 x 0.9 = 360A
For the fixed MCCBs, The In = Ir.
Categories of the Circuit Breakers
As per IEC 60947-2, there are two main selectivity categories. Those are Category A and B.
Category A: Mainly MCBs and some MCCBs comes under this category. In the event of a short circuit, they trip immediately.
Category B: Mainly MCCBs comes under this category. In the event of a short circuit, they will not trip immediately and hence allow the downstream circuit breaker to trip.
The Category A circuit breakers will be used for the protection of final circuits. The Category B circuit breakers will be used in MDBs, SMDBs and MCCs / MCPs.

Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.