What is MOCB
These types of circuit breakers utilize oil as the interrupting media. However, unlike bulk oil circuit breaker, a minimum oil circuit breaker places the interrupting unit in insulating chamber at live potential. The insulating oil is available only in interrupting chamber. The feature of designing MOCB is to reduce requirement of oil, and hence these breaker are called minimum oil circuit breaker.
As the volume of the oil in bulk oil circuit breaker is huge, the chances of fire hazard in bulk oil system are more. For avoiding unwanted fire hazard in the system, one important development in the design of oil circuit breaker has been introduced where use of oil in the circuit breaker is much less than that of bulk oil circuit breaker.
It has been decided that the oil in the circuit breaker should be used only as arc quenching media not as an insulating media. Then the concept of minimum oil circuit breaker comes. In this type of circuit breaker the arc interrupting device is enclosed in a tank of insulating material which as a whole is at live potential of system. This chamber is called arcing chamber or interrupting pot.
The gas pressure developed in the arcing chamber depends upon the current to be interrupted. Higher the current to be interrupted causes larger the gas pressure developed inside the chamber, hence better the arc quenching. But this put a limit on the design of the arc chamber for mechanical stresses.
With use of better insulating materials for the arcing chambers such as glass fiber, reinforced synthetic resin etc, the minimum oil circuit breaker are able to meet easily the increased fault levels of the system.
Working Principle or Arc Quenching in Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker
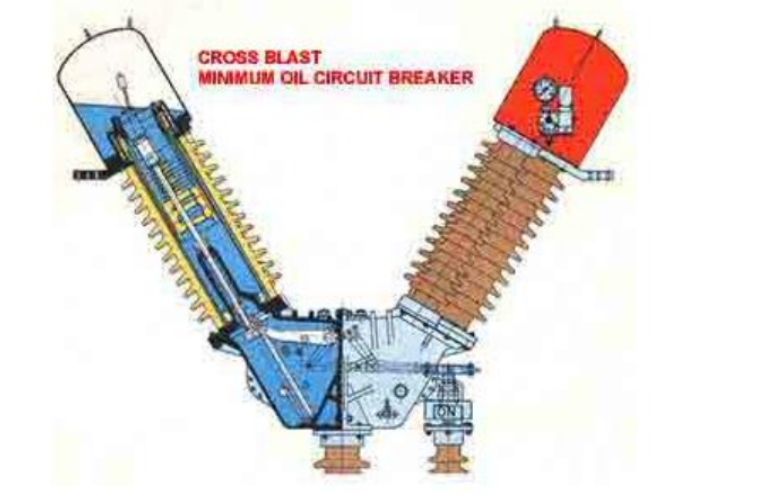
In a minimum oil circuit breaker, the arc drawn across the current carrying contacts is contained inside the arcing chamber. Hence the hydrogen bubble formed by the vaporized oil is trapped inside the chamber. As the contacts continue to move, after its certain travel an exit vent becomes available for exhausting the trapped hydrogen gas.
There are two different types of arcing chamber is available in terms of venting are provided in the arcing chambers. One is axial venting and other is radial venting. In axial venting, gases (mostly Hydrogen), produced due to vaporization of oil and decomposition of oil during arc, will sweep the arc in axial or longitudinal direction.
Let‟s have a look on working principle Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker with axial venting arc chamber. The moving contact has just been separated and arc is initiated in MOCB. The ionized gas around the arc sweep away through upper vent and cold oil enters into the arcing chamber through the lower vent in axial direction as soon as the moving contact tip crosses the lower vent opening and final arc quenching in minimum oil circuit breaker occurs the cold oil occupies the gap between fixed contact and moving contact and the minimum oil circuit breaker finally comes into open position.
Whereas in case of radial venting or cross blast, the gases (mostly Hydrogen) sweep the arc in radial or transverse direction. The axial venting generates high gas pressure and hence has high dielectric strength, so it is mainly used for interrupting low current at high voltage. On the other hand radial venting produces relatively low gas pressure and hence low dielectric strength so it can be used for low voltage and high current interruption.
Many times the combination of both is used in minimum oil circuit breaker so that the chamber is equally efficient to interrupt low current as well as high current. These types of circuit breaker are available up to 8000 MVA at 245 KV.