
In a world driven by technological innovation, Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) have emerged as pivotal components in ensuring electrical safety and efficiency. This compact yet powerful device is poised to revolutionize the way we manage electrical systems, ensuring safety, efficiency, and adaptability. So in this blog post, we explain What is MCB? It’s future technology.
Table of Contents
ToggleMCB Working principle
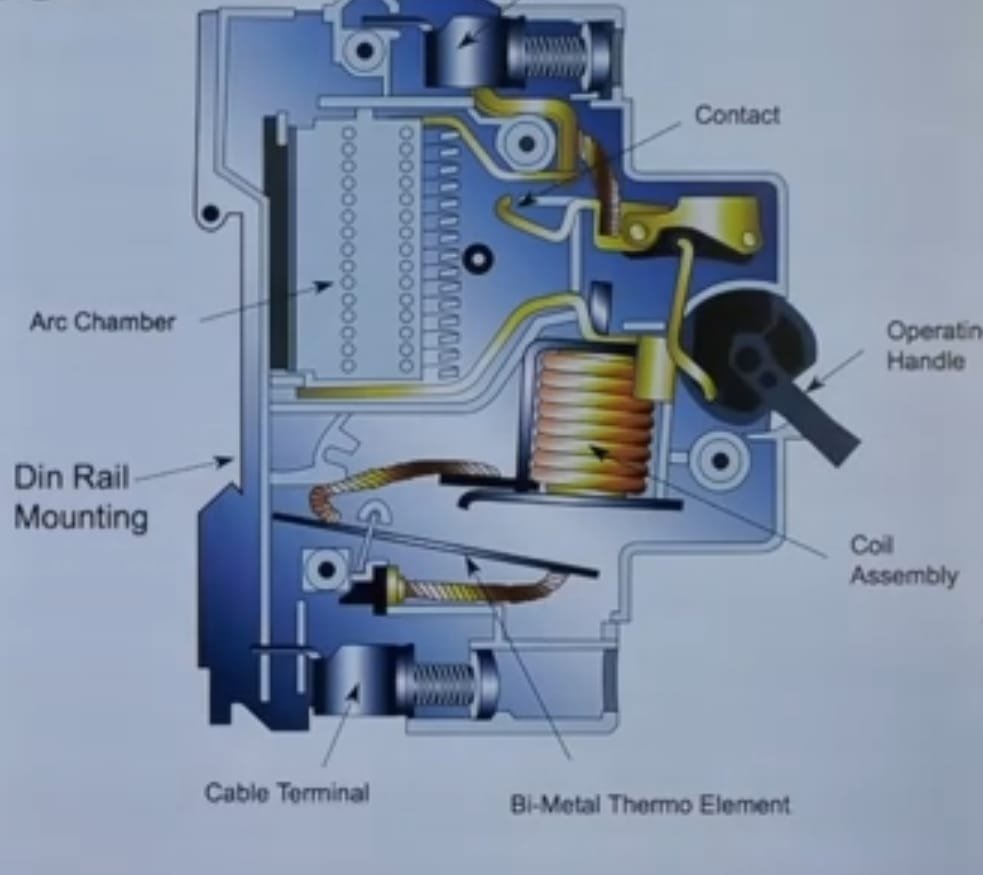
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is electrical device which secure electrical equipment in case of any short circuit or major fault.
There are two arrangement of operation of miniature circuit breaker. One due to thermal effect of over current and other due to electromagnetic effect of over current. The thermal operation of miniature circuit breaker is achieved with a bimetallic strip whenever continuous over current flows through MCB, the bimetallic strip is heated and deflects by bending
This deflection of bimetallic strip releases mechanical latch. As this mechanical latch is attached with operating mechanism, it causes to open the miniature circuit breaker contacts
But during short circuit condition, sudden rising of current, causes electromechanical displacement of plunger associated with tripping coil or solenoid of MCB. The plunger strikes the trip lever causing immediate release of latch mechanism consequently open the circuit breaker contacts.
Operating mechanism of miniature circuit breaker (MCB)
The operating mechanism of miniature circuit breaker provides the means of manual opening and closing operation of miniature circuit breaker. It has three-positions “ON,” “OFF,” and “TRIPPED”. The external switching latch can be in the “TRIPPED” position, if the MCB is tripped due to over-current. When manually switch off the MCB, the switching latch will be in “OFF” position.
In close condition of MCB, the switch is positioned at “ON”. By observing the positions of the switching latch one can determine the condition of MCB whether it is closed, tripped or manually switched off.
The TRIP Unit of the miniature circuit breaker (MCB)
The trip unit is the main part, responsible for proper working of miniature circuit breaker. Two main types of trip mechanism are provided in MCB. A bimetal provides protection against over load current and an electromagnet provides protection against short-circuit current.
Types of MCB
There are types of MCB based on their trip curves and based on number of poles.
Types of MCB Based on their Trip Curve
- Type B MCB
B types trip if the current flowing through hits between three and five times the recommended maximum. Type B is the most sensitive types of MCB, designed for domestic and low voltage commercial settings where any current surges are likely to be small like lighting circuits, home wirings, etc.
- Type C MCB
C types trip at currents between five and ten times their rated load. They find use in commercial or industrial types of applications where there could be chances of higher values of short circuit currents in the circuit. Good examples include smaller electric motors, fans, fluorescent lighting, small transformers, pilot devices, control circuits, coils, etc
- Type D MCB
D type MCBs are the least sensitive type, only activating when current surges to between ten and twenty times the recommended maximum. 4/8 Examples include welding equipment, X-ray machines, UPS systems, large motors, uninterruptible power supply units, industrial welding equipment, etc
- Type K MCB
Type K trip when the current reaches 8 to 12 times than the rated current with an operating time of less than 0.1 Second. These are used for inductive loads which have a chance of high inrush currents. They are also a good choice for motors
- Type Z MCB
Type Z MCBs are highly sensitive MCBs that operate for a current value between 2 to 3 times the rated current with an operating time of less than 0.1 Second. They are used with more delicate devices prone to short circuits, such as semiconductors.
Types of MCBs based on the number of poles
- Single Pole MCB
A single-pole circuit breaker has one switch and also protects a single phase of the circuit.
- Double pole MCB
The double pole circuit breaker has two switches and also protects two-phase and neutral.
- Triple Pole MCB
A three-pole circuit breaker has three switches, and they also protect the three phases
- Three poles with a neutral
Three poles and a neutral circuit breaker protect the three phases of the circuit. It also has a neutral switch
- Four Poles
A four-pole MCB contains four switches, three phases, and a neutral. But unlike the three poles with neutral, the four poles protect all the phases and the neutral. They are used in places with an unbalanced circuit.
What is MCB? It’s future technology-video tutorial
Ampere Rating of MCB
The current rating is the value of the current over which the breaker gets tripped. The Rated current of the MCB to be used depends on the load current of the equipment to be protected. For a typical MCB, this rating is 6 amp to 125 amp.
They are available in the following ratings: 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 45A, 50A, 63A, 80A, 100A, 125A.
For example, if you use AC in your house, then it is advisable to use a 20 amp MCB, and for regular lights and fans, 6 amp should do just fine. The following lists some of the most frequently encountered load capacities for commercial MCBs: 6 amps 10 amp, 16 amp, 20 amps 25 amp, 32 amp.
MCB vs Fuse
Nowadays miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) are much more commonly used in low voltage electrical networks instead of fuses. The MCB has many advantages compared to a fuse:
- It automatically switches off the electrical circuit during the abnormal conditions of the network (both overload and fault conditions). The MCB is much more reliable in the detection of such conditions, is it is more sensitive to change in current.
- As the switch operating knob comes at its off position during tripping, the faulty zone of the electrical circuit can easily be identified. But in case of a fuse, the fuse wire should be checked by opening fuse grip or cut out from fuse base, for confirming the blow of fuse wire. Thus, is it much detect if an MCB has been operated compared to a fuse.
- Quick restoration of supply cannot be possible in case of fuse, as fuses have to be rewirable or replaced for restoring the supply. But in the case of an MCB, quick restoration is possible by (literally) flipping a switch.
- The handling of an MCB is more electrically safe than a fuse.
- MCBs can be controlled remotely, whereas fuses cannot. Because of these many advantages of MCB over fuse units, in modern low voltage electrical network, the miniature circuit breaker is almost always used instead of a fuse.
Future technology of MCB
The future technology associated with MCBs involves advancements in smart and digital circuit breakers. These innovations enable remote monitoring, real-time data analysis, and enhanced control of electrical systems. Smart MCBs offer improved efficiency, increased safety, and the ability to monitor and manage electrical systems remotely. They can provide valuable insights into power consumption and help prevent electrical failures.Following application of MCB in future technology:
- Integration with IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) is playing a pivotal role in transforming various industries, and MCBs are no exception. In the future, MCBs are likely to be seamlessly integrated into IoT networks, allowing for advanced monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved energy management.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Future iterations of MCBs are expected to incorporate even more advanced safety features. These may include the ability to detect and respond to different types of electrical faults with greater precision, ensuring an unprecedented level of safety for electrical systems.
- Lighting Systems: Our homes are dominated by a wide range of lights. All these lights are in use for large parts of the day. This makes it essential to install an MCB via which effective distribution of power is made possible. Certain lights need more power than others, and MCBs can regulate accordingly and offer unique lightening systems the safety they need. This safeguarding of bulbs with MCBs ensures the longevity of bulbs
- Energy Efficiency: As the world shifts towards sustainable practices, MCB technology is likely to contribute to energy efficiency. Smart MCBs may optimize power distribution, identify energy wastage, and facilitate intelligent load shedding to reduce overall energy consumption.
Frequently Ask Question(FAQ)
1.What is full form of MCB?
Full form of MCB is Miniature Circuit Breaker.
2.What is MCB?
It is an electrical switch designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overload or short circuit.
- How does an MCB different from a fuse?
After tripping MCB can be reset and it can be reusable solution. While fuse can not use after fail or blown.
- Can we use AC MCB for DC?
Because of the different arc-burning and arc-extinguishing processes of AC and DC, the ability of AC and DC MCB with the same rated value to break DC power supply is not exactly the same. One of the main reasons for the protection of overstepping mistake operation is to use AC MCB instead of DC MCB.
- Does MCB trip automatically?
If any short circuit or ground fault occures, then due to high sure happen in system.When this occures, system MCB trip automatically.
6. What is difference between MCB and MCCB?
MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breakers, while MCCB is Molded Case Circuit Breaker. The main difference between the two is their capacity, with the MCB is mainly used for low-energy requirements, like home wiring or small electronic circuits. On the other hand, the MCCB is more suited in providing energy for high-power equipment. Generally, the MCB rated current is under 250 amps.
- How will MCB technology evolve in the coming years?
The future of MCB technology is likely to see further integration with smart home and industrial automation systems. Enhanced communication capabilities and increased energy efficiency are expected to be key focus areas for development.
- Can we repaired MCB ?
MCB built for better performance for protection of electrical system. Faulty mcb can not reliable for protection of electrical equipment. It means that you cannot repair a faulty MCB; it must be replaced.

Pingback: Understanding 11kV Vacuum Circuit Breaker(VCB) and VCB Panel in Detail
Pingback: Types of Circuit breaker used in Home and Industries
Pingback: Step for carried out estimate in Home wiring and selection of MCB
Pingback: What is Contactor and their working, types and application - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Types of Circuit Breaker and their working principle
Pingback: ELCB: Working principle, Full name and Circuit diagram - Electricalsphere
Pingback: DC distribution in 132 KV, 220 KV, 400 KV Control and Relay Panel in substation
Pingback: MCCB circuit Breaker and their application - Electricalsphere
Pingback: Distribution Transformer Failure: Cause, Analysis and Case study