Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of Railway Track Electrification
The three main types of electric traction systems that exist are as follows:
- Direct Current (DC) electrification system
- Alternating Current (AC) electrification system
- Composite system.
DC Electrification System
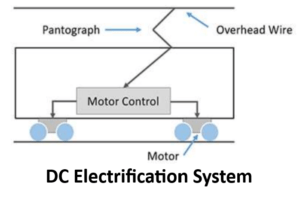
The choice of selecting DC electrification system encompasses many advantages, such as space and weight considerations, rapid acceleration and braking of DC electric motors, less cost compared to AC systems, less energy consumption and so on. In this type of system, three-phase power received from the power grids is de-escalated to low voltage and converted into DC by the rectifiers and power-electronic converters.
This type of DC supply is supplied to the vehicle through two different ways:
3rd and 4th rail system operate at low voltages (600-1200V)
Overhead rail systems use high voltages (1500-3000V)
The supply systems of DC electrification include:
300-500V supply for the special systems like battery systems.
600-1200V for urban railways like tramways and light metro trains.
1500-3000V for suburban and mainline services like light metros and heavy metro trains.
Due to high starting torque and moderate speed control, the DC series motors are extensively employed in the DC traction systems. They provide high torque at low speeds and low torque at high speeds.
AC Electrification System
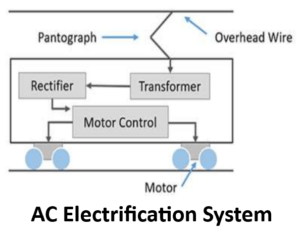
An AC traction system has become very popular nowadays, and it is more often used in most of the traction systems due to several advantages, such as quick availability and generation of AC that can be easily stepped up or down, easy controlling of AC motors, less number of substations requirement, and the presence of light overhead catenaries that transfer low currents at high voltages, and so on.
The supply systems of AC electrification include single, three phase, and composite systems. The Single phase systems consist of 11 to 15 KV supply at 16.7Hz, and 25Hz to facilitate variable speed to AC commutation motors. It uses step down transformer and frequency converters to convert from the high voltages and fixed industrial frequency.
The Single phase 25KV at 50Hz is the most commonly used configuration for AC electrification. It is used for heavy haul systems and main line services since it doesn’t require frequency conversion. This is one of the widely used types of composite systems wherein the supply is converted to DC to drive DC traction motors.
Three phase system uses three phase induction motor to drive the locomotive, and it is rated at 3.3.KV, 16.7Hz. The high-voltage distribution system at 50 Hz supply is converted to this electric motor rating by transformers and frequency converters. This system employs two overhead lines, and the track rail forms another phase, but this raises many problems at crossings and junctions.
Composite System
Composite System (or multi-system) trains are used to provide continuous journeys along routes that are electrified using more than one system. One way to accomplish this is by changing locomotives at the switching stations. These stations have overhead wires that can be switched from one voltage to another. Another way is to use multisystem locomotives that can operate under several different voltages and current types. In Europe, it is common to use four-system locomotives. (1.5 kV DC, 3 kV DC, 15 kV 16⅔ Hz AC, 25 kV 50 Hz AC).

Pingback: Faiveley type pantograph: Construction diagram and working - Electricalsphere
I love what you guys tend to be up too. Such clever work and exposure! Keep up the fantastic works guys I’ve included you guys to my personal blogroll.
I?¦ve read several good stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you set to create such a fantastic informative website.
Thanks a Lot!
Our aim is to provide information to all readers.
Share our content to yr friend group to encourage site.
Keep learning.
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your web site. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility problems? A handful of my blog audience have complained about my website not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Opera. Do you have any solutions to help fix this problem?
Well researched
Nicely put together
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!